前言¶
昨天盘点了一下目标检测算法的常见数据集还有评判标准,但目标检测过程还有一个后处理算法的重要性确常被忽略,今天我们就来盘点一下目标检测算法中的NMS相关知识吧。
NMS¶
介绍¶
非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression,NMS),顾名思义就是抑制不是极大值的元素。在目标检测任务,例如行人检测中,滑动窗口经过特征提取和分类器识别后,每个窗口都会得到一个分数。但滑动窗口会导致很多窗口和其它窗口存在包含大部分交叉的情况。这个时候就需要用到NMS来选取那些邻域里分数最高,同时抑制那些分数低的窗口。
原理¶
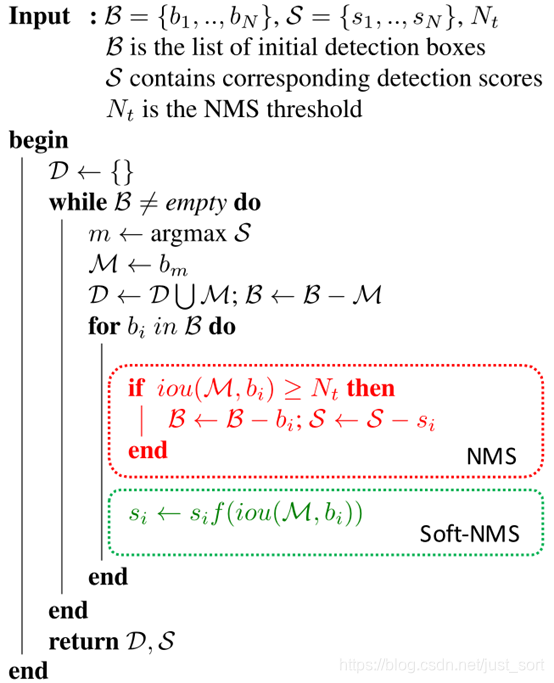
在目标检测任务中,定义最后的候选框集合为B,每个候选框对应的置信度是S,IOU阈值设为T,然后NMS的算法过程可以表示如下:
- 选择具有最大score的候选框M
- 将M从集合B中移除并加入到最终的检测结果D中
- 将B中剩余检测框中和M的交并比(IOU,昨天的推文有介绍)大于阈值T的框从B中移除
- 重复上面的步骤,直到B为空
代码实现¶
rgb大神实现Faster-RCNN中的单类别物体nms代码解释如下:
# --------------------------------------------------------
# Fast R-CNN
# Copyright (c) 2015 Microsoft
# Licensed under The MIT License [see LICENSE for details]
# Written by Ross Girshick
# --------------------------------------------------------
import numpy as np
def py_cpu_nms(dets, thresh):
"""Pure Python NMS baseline."""
#x1、y1、x2、y2、以及score赋值
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
scores = dets[:, 4]
#每一个检测框的面积
areas = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
#按照score置信度降序排序
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
#保留的结果框集合
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
#保留该类剩余box中得分最高的一个
keep.append(i)
# 得到相交区域,左上及右下
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[order[1:]])
#计算相交的面积,不重叠时面积为0
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
#计算IoU:重叠面积 /(面积1+面积2-重叠面积)
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
# 保留IoU小于阈值的box
inds = np.where(ovr <= thresh)[0]
# 因为ovr数组的长度比order数组少一个,所以这里要将所有下标后移一位
order = order[inds + 1]
return keep
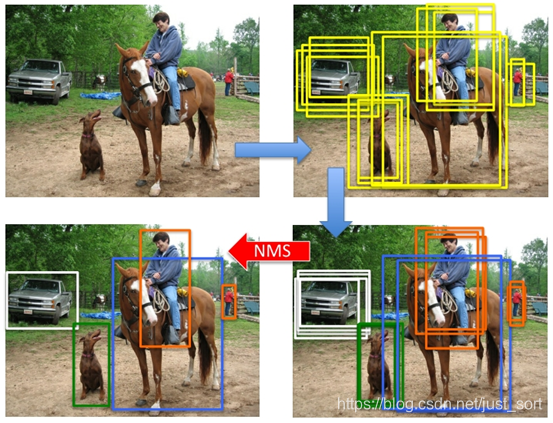
效果¶
Soft-NMS¶
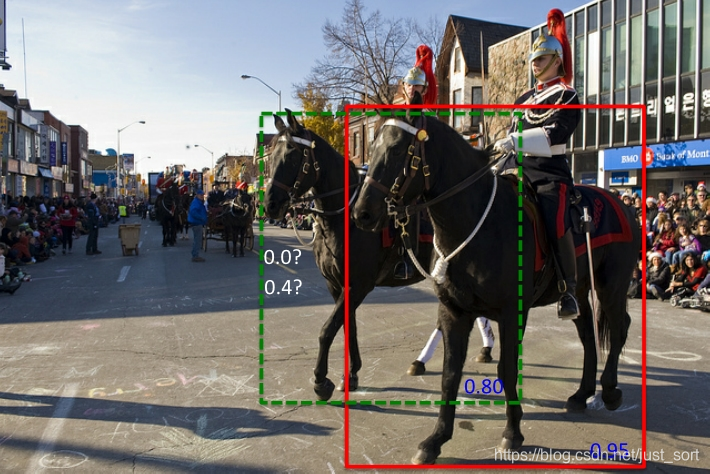
上面说的NMS算法有一个缺点就是当两个候选框的重叠度很高时,NMS会将具有较低置信度的框去掉,也就是将其置信度变成0,如下图所示,红色框和绿色框是当前的检测结果,二者的得分分别是0.95和0.80。如果按照传统的NMS进行处理,首先选中得分最高的红色框,然后绿色框就会因为与之重叠面积过大而被删掉。
因此为了改善这个缺点,Soft-NMS被提出,核心思路就是不要粗鲁地删除所有IOU大于阈值的框,而是降低其置信度。这个方法的论文地址为:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1704.04503.pdf 。算法伪代码如下:
正如作者所说,改一行代码就OK了。这里的f函数可以是线性函数,也可以是高斯函数。我们来对比一下: - 线性函数:
- 高斯函数: s_i=s_ie^{-{\text{iou}(\mathcal M,b_i)^2}\over \sigma},\forall b_i\not \in \mathcal D
代码实现¶
作者的代码如下:
def cpu_soft_nms(np.ndarray[float, ndim=2] boxes, float sigma=0.5, float Nt=0.3, float threshold=0.001, unsigned int method=0):
cdef unsigned int N = boxes.shape[0]
cdef float iw, ih, box_area
cdef float ua
cdef int pos = 0
cdef float maxscore = 0
cdef int maxpos = 0
cdef float x1,x2,y1,y2,tx1,tx2,ty1,ty2,ts,area,weight,ov
for i in range(N):
maxscore = boxes[i, 4]
maxpos = i
tx1 = boxes[i,0]
ty1 = boxes[i,1]
tx2 = boxes[i,2]
ty2 = boxes[i,3]
ts = boxes[i,4]
pos = i + 1
# get max box
while pos < N:
if maxscore < boxes[pos, 4]:
maxscore = boxes[pos, 4]
maxpos = pos
pos = pos + 1
# add max box as a detection
boxes[i,0] = boxes[maxpos,0]
boxes[i,1] = boxes[maxpos,1]
boxes[i,2] = boxes[maxpos,2]
boxes[i,3] = boxes[maxpos,3]
boxes[i,4] = boxes[maxpos,4]
# swap ith box with position of max box
boxes[maxpos,0] = tx1
boxes[maxpos,1] = ty1
boxes[maxpos,2] = tx2
boxes[maxpos,3] = ty2
boxes[maxpos,4] = ts
tx1 = boxes[i,0]
ty1 = boxes[i,1]
tx2 = boxes[i,2]
ty2 = boxes[i,3]
ts = boxes[i,4]
pos = i + 1
# NMS iterations, note that N changes if detection boxes fall below threshold
while pos < N:
x1 = boxes[pos, 0]
y1 = boxes[pos, 1]
x2 = boxes[pos, 2]
y2 = boxes[pos, 3]
s = boxes[pos, 4]
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
iw = (min(tx2, x2) - max(tx1, x1) + 1)
if iw > 0:
ih = (min(ty2, y2) - max(ty1, y1) + 1)
if ih > 0:
ua = float((tx2 - tx1 + 1) * (ty2 - ty1 + 1) + area - iw * ih)
ov = iw * ih / ua #iou between max box and detection box
if method == 1: # linear
if ov > Nt:
weight = 1 - ov
else:
weight = 1
elif method == 2: # gaussian
weight = np.exp(-(ov * ov)/sigma)
else: # original NMS
if ov > Nt:
weight = 0
else:
weight = 1
boxes[pos, 4] = weight*boxes[pos, 4]
# if box score falls below threshold, discard the box by swapping with last box
# update N
if boxes[pos, 4] < threshold:
boxes[pos,0] = boxes[N-1, 0]
boxes[pos,1] = boxes[N-1, 1]
boxes[pos,2] = boxes[N-1, 2]
boxes[pos,3] = boxes[N-1, 3]
boxes[pos,4] = boxes[N-1, 4]
N = N - 1
pos = pos - 1
pos = pos + 1
keep = [i for i in range(N)]
return keep
效果¶
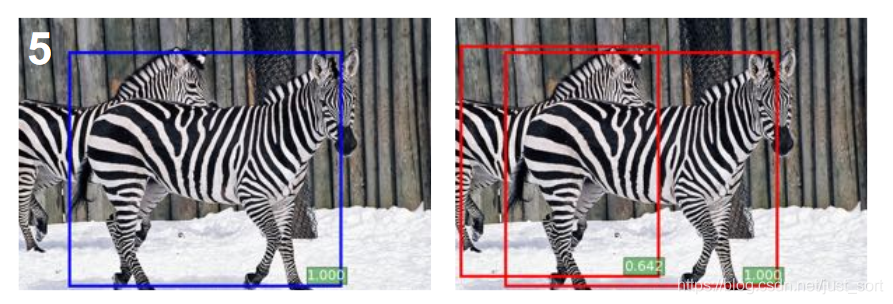 左边是使用了NMS的效果,右边是使用了Soft-NMS的效果。
左边是使用了NMS的效果,右边是使用了Soft-NMS的效果。
论文的实验结果¶
 可以看到在MS-COCO数据集上
可以看到在MS-COCO数据集上map$[0.5:0.95]可以获得大约1%的提升,如果应用到训练阶段的proposal选取过程理论上也能获得提升。顺便说一句,soft-NMS在不是基于Proposal的方法如SSD,YOLO中没什么提升。这里猜测原因可能是因为YOLO和SSD产生的框重叠率较低引起的。
后记¶
今天介绍了目标检测任务中的后处理过程最重要的NMS算法以及它的改进方案Soft-NMS算法,并提供了实现源码,希望大家能彻底理解这两个算法。
思考¶
NMS的阈值是否可以自适应?
欢迎关注我的微信公众号GiantPadaCV,期待和你一起交流机器学习,深度学习,图像算法,优化技术,比赛及日常生活等。
本文总阅读量次