1. 前言¶
在2月10日,Faster RCNN专栏由pprp同学起了个头,文章地址见这里:【Faster R-CNN】1. 梳理Faster R-CNN的四个模块,本着对公众号的每个专栏负责任的态度,我将在接下来的时间里将整个Faster RCNN的原理以及代码(陈云大佬的:https://github.com/chenyuntc/simple-faster-rcnn-pytorch)按照我的理解讲清楚并结束这个专题。
2. Faster RCNN整体结构¶
Faster RCNN的背景,介绍这些都没必要再次讲解了,这里我们直接再来复习一下Faster RCNN的整体结构,如下图所示。
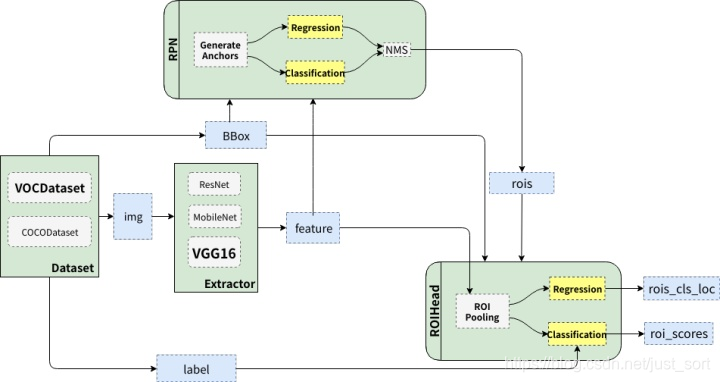
可以看到Faster RCNN大概可以分成绿色描述的4个部分,即:
- DataSet:代表数据集,典型的比如VOC和COCO。
- Extrator:特征提取器,也即是我们常说的Backbone网络,典型的有VGG和ResNet。
- RPN:全称Region Proposal Network,负责产生候选区域(rois),每张图大概给出2000个候选框。
- RoIHead:负责对rois进行分类和回归微调。
所以Faster RCNN的流程可以总结为:
原始图像--->特征提取------>RPN产生候选框------>对候选框进行分类和回归微调。
3. 数据预处理及实现细节¶
首先让我们进入到这个Pytorch的Faster RCNN工程:https://github.com/chenyuntc/simple-faster-rcnn-pytorch。数据预处理的相关细节都在data这个文件夹下面,我画了一个流程图总结了Faster RCNN的预处理,如下:
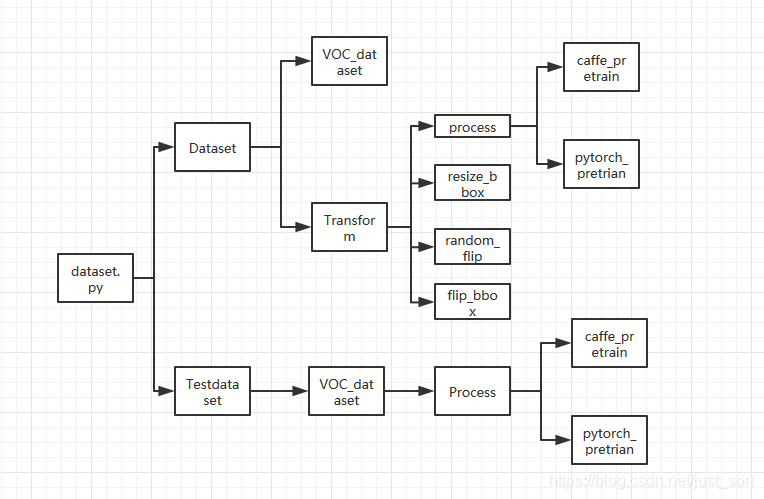
接下来我们结合一下我的代码注释来理解一下,首先是data/dataset.py。
# 去正则化,img维度为[[B,G,R],H,W],因为caffe预训练模型输入为BGR 0-255图片,pytorch预训练模型采用RGB 0-1图片
def inverse_normalize(img):
if opt.caffe_pretrain:
# [122.7717, 115.9465, 102.9801]reshape为[3,1,1]与img维度相同就可以相加了,
# pytorch_normalize之前有减均值预处理,现在还原回去。
img = img + (np.array([122.7717, 115.9465, 102.9801]).reshape(3, 1, 1))
# 将BGR转换为RGB图片(python [::-1]为逆序输出)
return img[::-1, :, :]
# pytorch_normalze中标准化为减均值除以标准差,现在乘以标准差加上均值还原回去,转换为0-255
return (img * 0.225 + 0.45).clip(min=0, max=1) * 255
# 采用pytorch预训练模型对图片预处理,函数输入的img为0-1
def pytorch_normalze(img):
"""
https://github.com/pytorch/vision/issues/223
return appr -1~1 RGB
"""
# #transforms.Normalize使用如下公式进行归一化
# channel=(channel-mean)/std,转换为[-1,1]
normalize = tvtsf.Normalize(mean=[0.485, 0.456, 0.406],
std=[0.229, 0.224, 0.225])
# nddarry->Tensor
img = normalize(t.from_numpy(img))
return img.numpy()
# 采用caffe预训练模型时对输入图像进行标准化,函数输入的img为0-1
def caffe_normalize(img):
"""
return appr -125-125 BGR
"""
# RGB-BGR
img = img[[2, 1, 0], :, :] # RGB-BGR
img = img * 255
# 转换为与img维度相同
mean = np.array([122.7717, 115.9465, 102.9801]).reshape(3, 1, 1)
# 减均值操作
img = (img - mean).astype(np.float32, copy=True)
return img
# 函数输入的img为0-255
def preprocess(img, min_size=600, max_size=1000):
# 图片进行缩放,使得长边小于等于1000,短边小于等于600(至少有一个等于)。
# 对相应的bounding boxes 也也进行同等尺度的缩放。
C, H, W = img.shape
scale1 = min_size / min(H, W)
scale2 = max_size / max(H, W)
# 选小的比例,这样长和宽都能放缩到规定的尺寸
scale = min(scale1, scale2)
img = img / 255.
# resize到(H * scale, W * scale)大小,anti_aliasing为是否采用高斯滤波
img = sktsf.resize(img, (C, H * scale, W * scale), mode='reflect',anti_aliasing=False)
#调用pytorch_normalze或者caffe_normalze对图像进行正则化
if opt.caffe_pretrain:
normalize = caffe_normalize
else:
normalize = pytorch_normalze
return normalize(img)
class Transform(object):
def __init__(self, min_size=600, max_size=1000):
self.min_size = min_size
self.max_size = max_size
def __call__(self, in_data):
img, bbox, label = in_data
_, H, W = img.shape
# 图像等比例缩放
img = preprocess(img, self.min_size, self.max_size)
_, o_H, o_W = img.shape
# 得出缩放比因子
scale = o_H / H
# bbox按照与原图等比例缩放
bbox = util.resize_bbox(bbox, (H, W), (o_H, o_W))
# 将图片进行随机水平翻转,没有进行垂直翻转
img, params = util.random_flip(
img, x_random=True, return_param=True)
# 同样地将bbox进行与对应图片同样的水平翻转
bbox = util.flip_bbox(
bbox, (o_H, o_W), x_flip=params['x_flip'])
return img, bbox, label, scale
# 训练集样本的生成
class Dataset:
def __init__(self, opt):
self.opt = opt
# 实例化类
self.db = VOCBboxDataset(opt.voc_data_dir)
#实例化类
self.tsf = Transform(opt.min_size, opt.max_size)
# __ xxx__运行Dataset类时自动运行
def __getitem__(self, idx):
# 调用VOCBboxDataset中的get_example()从数据集存储路径中将img, bbox, label, difficult 一个个的获取出来
ori_img, bbox, label, difficult = self.db.get_example(idx)
# 调用前面的Transform函数将图片,label进行最小值最大值放缩归一化,
# 重新调整bboxes的大小,然后随机反转,最后将数据集返回
img, bbox, label, scale = self.tsf((ori_img, bbox, label))
# TODO: check whose stride is negative to fix this instead copy all
# some of the strides of a given numpy array are negative.
return img.copy(), bbox.copy(), label.copy(), scale
def __len__(self):
return len(self.db)
# 测试集样本的生成
class TestDataset:
def __init__(self, opt, split='test', use_difficult=True):
self.opt = opt
# 此处设置了use_difficult,
self.db = VOCBboxDataset(opt.voc_data_dir, split=split, use_difficult=use_difficult)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
ori_img, bbox, label, difficult = self.db.get_example(idx)
img = preprocess(ori_img)
return img, ori_img.shape[1:], bbox, label, difficult
def __len__(self):
return len(self.db)
接下来是data/voc_dataset.py,注释如下:
class VOCBboxDataset:
def __init__(self, data_dir, split='trainval',
use_difficult=False, return_difficult=False,
):
# if split not in ['train', 'trainval', 'val']:
# if not (split == 'test' and year == '2007'):
# warnings.warn(
# 'please pick split from \'train\', \'trainval\', \'val\''
# 'for 2012 dataset. For 2007 dataset, you can pick \'test\''
# ' in addition to the above mentioned splits.'
# )
# id_list_file为split.txt,split为'trainval'或者'test'
id_list_file = os.path.join(
data_dir, 'ImageSets/Main/{0}.txt'.format(split))
# id_为每个样本文件名
self.ids = [id_.strip() for id_ in open(id_list_file)]
# 写到/VOC2007/的路径
self.data_dir = data_dir
self.use_difficult = use_difficult
self.return_difficult = return_difficult
# 20类
self.label_names = VOC_BBOX_LABEL_NAMES
# trainval.txt有5011个,test.txt有210个
def __len__(self):
return len(self.ids)
def get_example(self, i):
#读入xml标签文件
id_ = self.ids[i]
anno = ET.parse(
os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'Annotations', id_ + '.xml'))
bbox = list()
label = list()
difficult = list()
#解析xml文件
for obj in anno.findall('object'):
# 标为difficult的目标在测试评估中一般会被忽略
if not self.use_difficult and int(obj.find('difficult').text) == 1:
continue
#xml文件中包含object name和difficult(0或者1,0代表容易检测)
difficult.append(int(obj.find('difficult').text))
# bndbox(xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax),表示框左下角和右上角坐标
bndbox_anno = obj.find('bndbox')
# #让坐标基于(0,0)
bbox.append([
int(bndbox_anno.find(tag).text) - 1
for tag in ('ymin', 'xmin', 'ymax', 'xmax')])
# 框中object name
name = obj.find('name').text.lower().strip()
label.append(VOC_BBOX_LABEL_NAMES.index(name))
# 所有object的bbox坐标存在列表里
bbox = np.stack(bbox).astype(np.float32)
# 所有object的label存在列表里
label = np.stack(label).astype(np.int32)
# PyTorch 不支持 np.bool,所以这里转换为uint8
difficult = np.array(difficult, dtype=np.bool).astype(np.uint8)
# 根据图片编号在/JPEGImages/取图片
img_file = os.path.join(self.data_dir, 'JPEGImages', id_ + '.jpg')
# 如果color=True,则转换为RGB图
img = read_image(img_file, color=True)
# if self.return_difficult:
# return img, bbox, label, difficult
return img, bbox, label, difficult
# 一般如果想使用索引访问元素时,就可以在类中定义这个方法(__getitem__(self, key) )
__getitem__ = get_example
# 类别和名字对应的列表
VOC_BBOX_LABEL_NAMES = (
'aeroplane',
'bicycle',
'bird',
'boat',
'bottle',
'bus',
'car',
'cat',
'chair',
'cow',
'diningtable',
'dog',
'horse',
'motorbike',
'person',
'pottedplant',
'sheep',
'sofa',
'train',
'tvmonitor')
再接下来是utils.py里面一些用到的相关函数的注释,只选了其中几个,并且有一些函数没有用到,全部放上来篇幅太多:
def resize_bbox(bbox, in_size, out_size):
# 根据图片resize的情况来缩放bbox
bbox = bbox.copy()
# #获得与原图同样的缩放比
y_scale = float(out_size[0]) / in_size[0]
x_scale = float(out_size[1]) / in_size[1]
# #按与原图同等比例缩放bbox
bbox[:, 0] = y_scale * bbox[:, 0]
bbox[:, 2] = y_scale * bbox[:, 2]
bbox[:, 1] = x_scale * bbox[:, 1]
bbox[:, 3] = x_scale * bbox[:, 3]
return bbox
def flip_bbox(bbox, size, y_flip=False, x_flip=False):
# 根据图片flip的情况来flip bbox
H, W = size #缩放后图片的size
bbox = bbox.copy()
if y_flip: #进行垂直翻转
y_max = H - bbox[:, 0]
y_min = H - bbox[:, 2]
bbox[:, 0] = y_min
bbox[:, 2] = y_max
if x_flip: #进行水平翻转
x_max = W - bbox[:, 1]
x_min = W - bbox[:, 3] #计算水平翻转后左下角和右上角的坐标
bbox[:, 1] = x_min
bbox[:, 3] = x_max
return bbox
def random_flip(img, y_random=False, x_random=False,
return_param=False, copy=False):
# 数据增强,随机翻转
y_flip, x_flip = False, False
if y_random:
y_flip = random.choice([True, False])
# 随机选择图片是否进行水平翻转
if x_random:
x_flip = random.choice([True, False])
if y_flip:
img = img[:, ::-1, :]
if x_flip:
# python [::-1]为逆序输出,这里指水平翻转
img = img[:, :, ::-1]
if copy:
img = img.copy()
if return_param:
#返回img和x_flip(为了让bbox有同样的水平翻转操作)
return img, {'y_flip': y_flip, 'x_flip': x_flip}
else:
return img
至此,我们就可以很好的理解数据预处理部分了,这部分也是最简单的,下一节我们开始搭建模型。带注释的Faster RCNN完整代码版本等我更新完这个专题我再放出来。
4. 思考¶
可以看到在Faster RCNN的代码中,数据预处理是相对简单的,没有大量的增强操作(相比于YOLOV3来说),如果结合更多的数据增强操作是否可以获得更好的精度呢?感觉值得尝试一下。
5. 附录¶
欢迎关注GiantPandaCV, 在这里你将看到独家的深度学习分享,坚持原创,每天分享我们学习到的新鲜知识。( • ̀ω•́ )✧
有对文章相关的问题,或者想要加入交流群,欢迎添加BBuf微信:

本文总阅读量次