【BBuf的CUDA笔记】七,总结 FasterTransformer Decoder(GPT) 的cuda相关优化技巧
这里总结 FasterTransformer Decoder(GPT) 的cuda相关优化技巧¶
解读:https://github.com/NVIDIA/FasterTransformer/blob/main/docs/gpt_guide.md
FasterTransformer GPT¶
这篇文档讲了一下 FasterTransformer 为 GPT 模型提供了什么,解释了工作流程和优化。并且还提供了在 FastTransformer 上运行 GPT 模型的指南。最后还提供了 Benchmark 测试来说明 FastTransformer 在 GPT 模型上的性能。我这里只针对 FasterTransformer GPT 的工作流程和做的优化进行讲解。
下面的 FasterTransformer GPT 介绍 和 FasterTransformer GPT 结构是简单翻了下文档。
FasterTransformer GPT 介绍(翻译)¶
GPT 是 Decooding 模型的一种变体,没有 Encoder 模块,没有交叉多头注意力模块,使用 GeLU 作为激活函数。2020 年,OpenAI 在他们的论文中表明,使用非常庞大的模型和大量的训练数据可以显著提高 GPT 模型的容量。 但是,不可能将这样的模型放入单个 GPU 中。 例如,最大的模型 GPT-3 有 1750 亿个参数,half 数据类型下大约需要 350 GB显存。 因此,多GPU,甚至多节点,是很有必要的。 为了解决模型大小导致的延迟和内存瓶颈,FasterTransformer 提供了高性能、低内存占用的 kernel,并使用了模型并行技术。
支持的特性¶
- Checkpoint converter
- Huggingface
- Megatron
- Nemo Megatron
- TensorFlow
- Data type
- FP32
- FP16
- BF16
- INT8 weight only PTQ.
- 限制:
- 权重被切分后,隐藏层的维度必须是 64 的倍数。
- cuda kernel通常只为小的 batch(如32和64)和权重矩阵很大时提供性能优势。
- 权重的 PTQ 量化只支持 FP16/BF16。
- 仅支持 Volta 和更新的 GPU 架构。
- Note:
- 根据当前 GPU 的情况,权重被提前离线预处理,以降低 TensorCore 做权重对齐的开销。目前,我们直接使用 FP32/BF16/FP16 权重并在推理前对其进行量化。如果我们想存储量化的权重,必须要在推理的 GPU 上来进行预处理。
- 使用 torch API 时,int8 模式只能通过 Parallel GPT Op 使用。 Parallel GPT Op 也可以在单个 GPU 上使用。
- INT8 with SmoothQuant
- FP8 (Experimental)
- Feature
- Multi-GPU multi-node inference
- Dynamic random seed
- Stop tokens
- Beam search and sampling are both supported
- Loading FP32 or FP16 weights
- Frameworks
- TensorFlow
- PyTorch
- C++
- Triton backend
FasterTransformer GPT 结构(翻译)¶
工作流¶
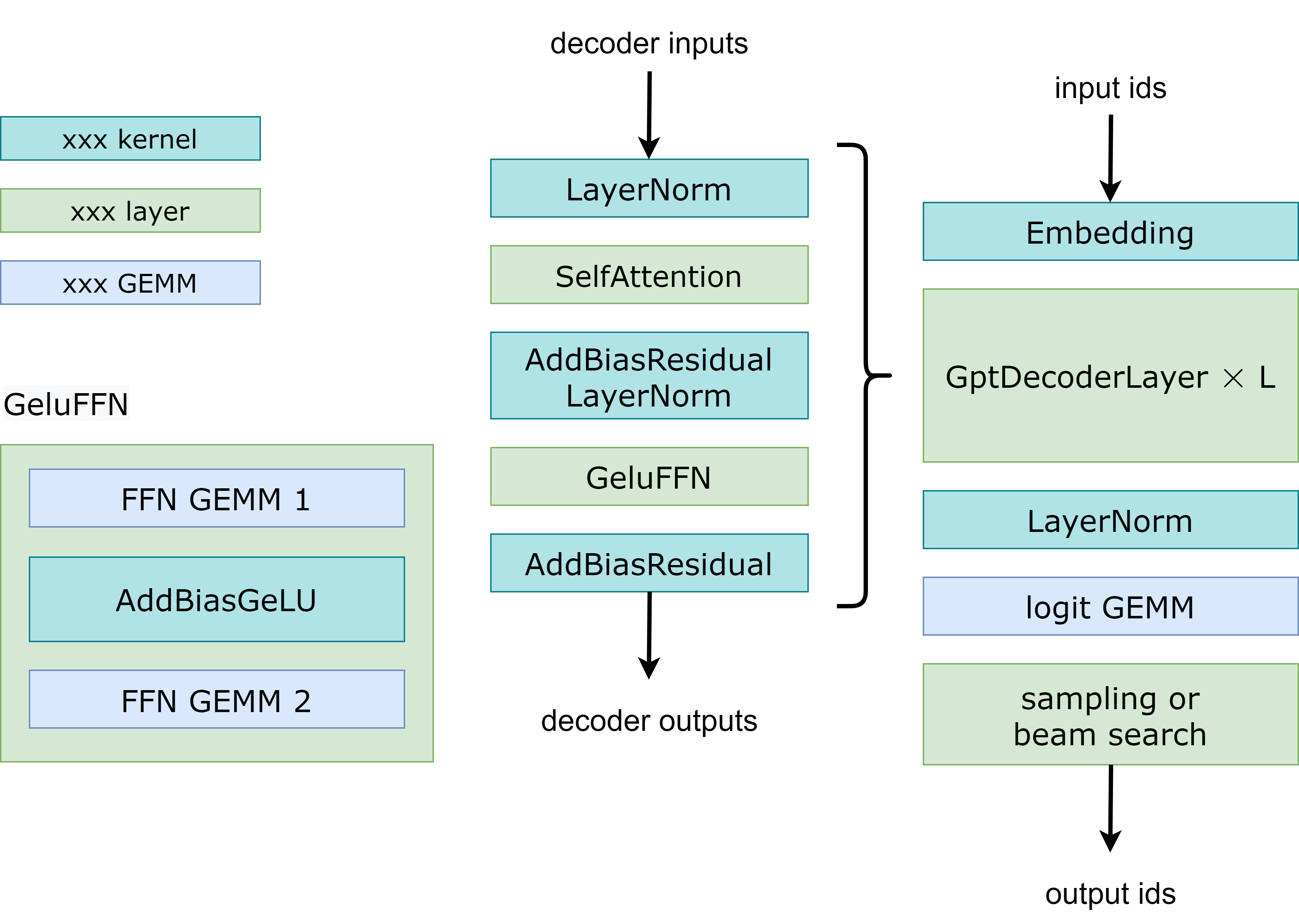
Fig 1展示了 FasterTransformer GPT 的工作流程。 与 BERT 和编码器-解码器结构不同,GPT 接收一些输入 id 作为上下文,并生成相应的输出 id 作为响应。在这个工作流中,主要的瓶颈是 GptDecoderLayer (Transformer块),因为当我们增加层数的时候耗时也是线性增加的。在GPT-3中,GptDecoderLayer占用了大约95%的时间。
FasterTransformer把整个工作流分成了两个部分。第一个部分是:“根据上下文context(也就是输入ids)计算k/v cache”。第二个部分是:“自回归的生成输出ids”。这两部分的操作类似,但是selfAttention部分的输入tensors的形状是不一样的。所以FasterTransformer提供了2种计算方式,如Fig2所示。在DecoderSelfAttention里面,query的序列长度总是1,所以我们使用自定义的fused masked multi-head attention kernel 进行处理。另一方面,在ContextSelfAttention中,query的序列长度最大时输入的长度,所以我们使用cuBLAS来利用TensorCore。
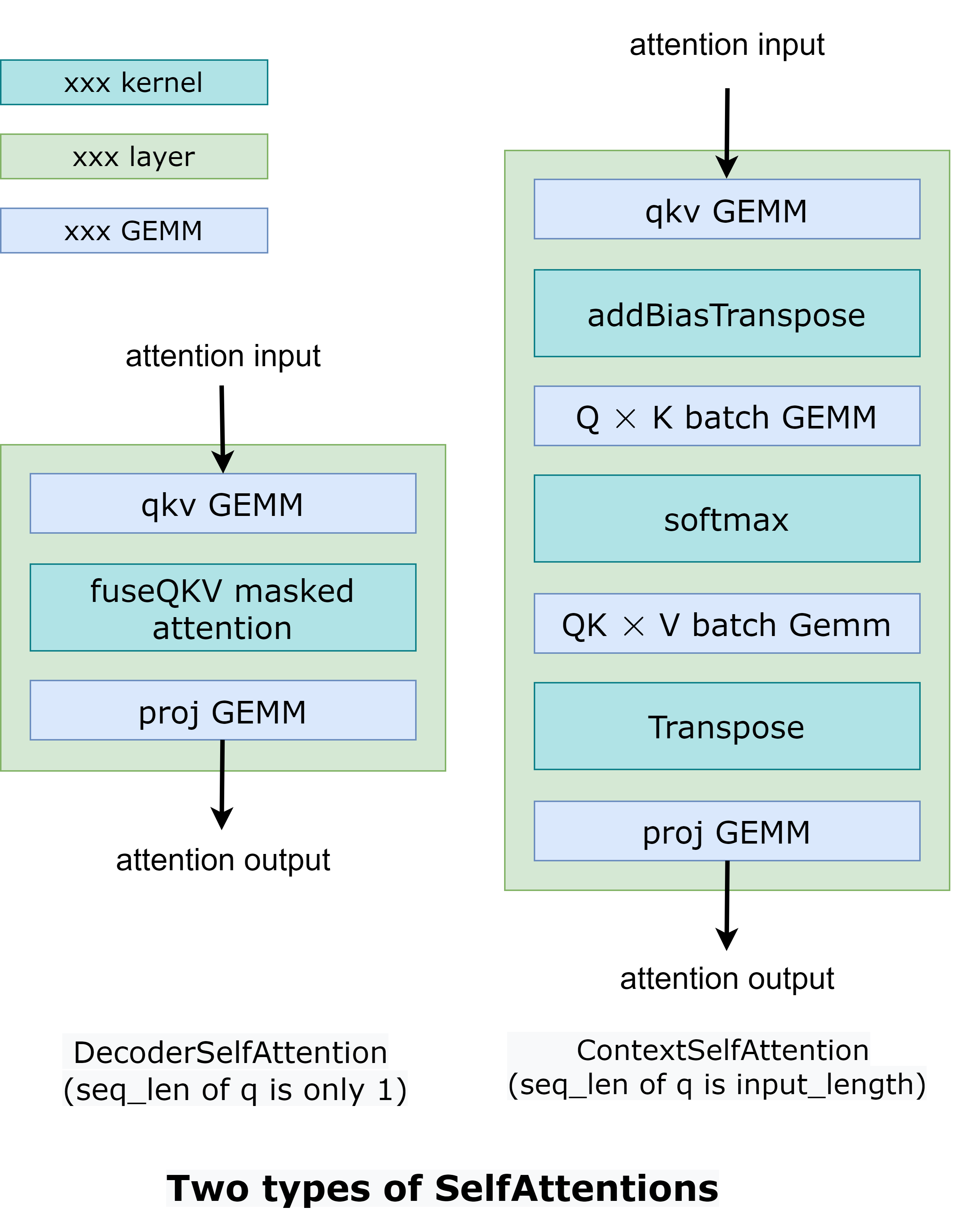
这个地方没有理解为什么要分成2个Attention,因为自回归的解码也是需要把输入的句子 padding 到最大的长度吧。这里的seq_len为1的情况是什么时候发生呢?我看了一下hugging face的GPT,似乎没有找到对应的位置。然后在FasterTransformer的GPT C++实现中也没有找到这个DecoderSelfAttention的实现:https://github.com/NVIDIA/FasterTransformer/blob/main/src/fastertransformer/models/multi_gpu_gpt/ParallelGptContextDecoder.cc 。不过本文主要是在后面介绍下 FasterTransformer 的优化点以及优缺点,这个暂时不影响解读。
以下示例演示如何运行多 GPU 和多节点 GPT 模型。
examples/cpp/multi_gpu_gpt_example.cc: 它使用 MPI 来组织所有 GPU。examples/cpp/multi_gpu_gpt_triton_example.cc: 它在节点内使用多线程,节点间使用 MPI。此示例还演示了如何使用 FasterTransformer 的 Triton 后端 API 来运行 GPT 模型。examples/pytorch/gpt/multi_gpu_gpt_example.py: 这个例子和examples/cpp/multi_gpu_gpt_example.cc很类似, 但是通过 PyTorch OP 封装了 FasterTransformer 的实例。
总之,运行 GPT 模型的工作流程是:
- 通过 MPI 或多线程初始化 NCCL 通信并设置张量并行和流水并行的等级。
- 按张量并行、流水并行的ranks和其它模型超参数加载权重。
- 按张量并行,流水并行的ranks和其它模型超参数创建
ParalelGpt实例。 - 接收来自客户端的请求并将请求转换为ParallelGpt的输入张量格式.
- 运行 forward 函数
- 将 ParallelGpt 的输出张量转换为客户端的响应并返回响应。
在c++示例代码中,我们跳过第4步和第6步,通过examples/cpp/multi_gpu_gpt/start_ids.csv加载请求。 在 PyTorch 示例代码中,请求来自 PyTorch 端。 在 Triton 示例代码中,我们有从步骤 1 到步骤 6 的完整示例。
源代码放在 src/fastertransformer/models/multi_gpu_gpt/ParallelGpt.cc 中。 GPT的参数、输入张量和输出张量:
- Constructor of GPT
| Classification | Name | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| [0] | max_batch_size | size_t | Deprecated, move to input |
| [1] | max_seq_len | size_t | Deprecated, move to input |
| [2] | max_input_len | size_t | Deprecated, move to input |
| [3] | beam_width | size_t | Deprecated, move to input |
| [4] | head_num | size_t | Head number for model configuration |
| [5] | size_per_head | size_t | Size per head for model configuration |
| [6] | inter_size | size_t | The inter size of feed forward network. It is often set to 4 * head_num * size_per_head. |
| [7] | num_layer | size_t | Number of transformer layers for model configuration |
| [8] | vocab_size | int | Vocabulary size for model configuration |
| [9] | start_id | int | Start id for vocabulary |
| [18] | temperature | float | Deprecated, move to input |
| [19] | len_penalty | float | Deprecated, move to input |
| [20] | repetition_penalty | float | Deprecated, move to input |
| [21] | tensor_para | NcclParam | Tensor Parallel information, which is declared in src/fastertransformer/utils/nccl_utils.h |
| [22] | pipeline_para | NcclParam | Pipeline Parallel information, which is declared in src/fastertransformer/utils/nccl_utils.h |
| [23] | stream | cudaStream_t | CUDA stream |
| [24] | cublas_wrapper | cublasMMWrapper* | Pointer of cuBLAS wrapper, which is declared in src/fastertransformer/utils/cublasMMWrapper.h |
| [26] | is_free_buffer_after_forward | bool | 如果设置为 true,FasterTransformer 将在 forward 前分配缓冲区,并在 forward 后释放缓冲区。 当分配器基于内存池时,设置为“true”可能有助于减少推理期间的内存使用。 |
| [27] | cuda_device_prop | cudaDeviceProp* | CUDA 设备属性指针,用于获取共享内存大小等硬件属性 |
| [28] | sparse | bool | Is using sparsity. Experimental feature |
| [29] | int8_mode | int | 0 means no quantization. 1 means use weight-only PTQ Experimental feature. 2 for weight and activation quantization Experimental feature. |
| [30] | custom_all_reduce_comm | AbstractCustomComm | Custom all reduction communication for custom all reduction in model parallelism. It is only supported in 8-way tensor parallelism |
| [31] | enable_custom_all_reduce | int | Flag of enabling custom all reduction or not |
| [32] | remove_padding | bool | Remove the padding of input ids or not in context phase. |
| [33] | shared_contexts_ratio | float | 控制共享上下文优化使用的比率。If the compact size (that accounts only for unique prompts) is less than ratio * batch size,使用优化的实现 。 设置 shared_contexts_ratio=0 停用优化。 |
- Input of GPT
| Name | Tensor/Parameter Shape | Location | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| input_ids | [batch_size, max_input_length] | GPU | int | The input ids (context) |
| input_lengths | [batch_size] | GPU | int | The lengths of input ids |
| prompt_learning_task_name_ids | [batch_size] | CPU | int | Optional. Task name ids for prompt learning. |
| output_seq_len | [batch_size] | CPU | uint32_t | The largest number of tokens you hope for results. Note that it contains the input length |
| stop_words_list | [batch_size, 2, stop_words_length] | GPU | int | Optional. When FT generates words in this list, it will stop the generation. An extension of stop id |
| bad_words_list | [batch_size, 2, bad_words_length] | GPU | int | Optional. The words in the list will never be sampled. |
| repetition_penalty | [1] or [batch_size] | CPU | float | Optional. Repetition penalty applied to logits for both beam search and sampling. Exclusive with presence_penalty. |
| presence_penalty | [1] or [batch_size] | CPU | float | Optional. Presence penalty - additive type of repetition penalty - applied to logits for both beam search and sampling. Exclusive with repetition_penalty. |
| min_length | [1] or [batch_size] | CPU | int | Optional. Minimum number of tokens to generate |
| random_seed | [1] or [batch_size] | CPU | unsigned long long int | Optional. Random seed to initialize the random table in sampling. |
| request_prompt_lengths | [batch_size], | GPU | int | Optional. Length of prefix soft prompt embedding. This describes how many tokens of soft prompt embedding in each sentence. |
| request_prompt_embedding | [batch_size, max_prompt_length, hidden_units] | GPU | float/half/bfloat16 | Optional. FT will concat them with results of embedding lookup kernel. For prefix soft prompt embedding, the type must be float; for p/prompt tuning, the type is same to weight. |
| request_prompt_type | [batch_size] | CPU | int | Optional. Prompt type of request. This is necessary when user pass the prompt embedding by input |
| is_return_context_cum_log_probs | [1] | CPU | bool | Optional. Return the cumulative log probability of context or not |
| is_return_context_embeddings | [1] | CPU | bool | Optional. Return the sum of context tokens encodings or not |
| session_len | [1] | CPU | uint32 | Optional. The maximum time length allowed during the whole interactive generation. Only used for interactive generation feature |
| continue_gen | [1] | CPU | bool | Optional. A flag to tell FasterTransformer to not discard previous tokens and continue producing token based on previous generations. Only used for interactive generation feature |
| memory_len | [1] | CPU | uint32 | Optional. The maximum time memory used in attention modules. Reduces the memory footprint but quality of generation might degrades. |
| top_p_decay | [batch_size] | GPU | float | Optional. decay values for top_p sampling |
| top_p_min | [batch_size] | GPU | float | Optional. min top_p values for top p sampling |
| top_p_reset_ids | [batch_size] | GPU | uint32 | Optional. reset ids for resetting top_p values for top p sampling |
- Output of GPT
| Name | Tensor/Parameter Shape | Location | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| output_ids | [batch_size, beam_width, max_output_seq_len] | GPU | int | The output ids. It contains the input_ids and generated ids |
| sequence_length | [batch_size, beam_width] | GPU | int | The lengths of output ids |
| output_log_probs | [batch_size, beam_width, request_output_seq_len] | GPU | float | Optional. It records the log probability of logits at each step for sampling. |
| cum_log_probs | [batch_size, beam_width] | GPU | float | Optional. Cumulative log probability of generated sentences |
| context_embeddings | [batch_size, beam_width, hidden_units] | GPU | float | Optional. Sum of context tokens encodings. |
beam_width 值直接由输出形状设置。 当output_ids的beam_width大于1时,FT会使用beam search来生成token; 否则,FT 将使用 topk 或 topp 采样。 当 beam search 和 sampling 的输入无效时,比如 beam width 1,top k 0,top p 0.0,FT 会自动运行 greedy search。·
优化¶
- kernel 优化:很多 kernel 都是基于已经高度优化的解码器和解码模块的 kernel。 为了防止重新计算以前的key 和 value,我们将在每一步分配一个缓冲区来存储它们。 虽然它需要一些额外的内存使用,但我们可以节省重新计算的成本,在每一步分配缓冲区以及串行的成本。
- 内存优化:与 BERT 等传统模型不同,GPT-3 有 1750 亿个参数,即使我们以半精度存储模型也需要 350 GB。 因此,我们必须减少其他部分的内存使用。 在 FasterTransformer 中,我们将重用不同解码器层的内存缓冲区。 由于 GPT-3 的层数是 96,我们只需要 1/96 的内存。
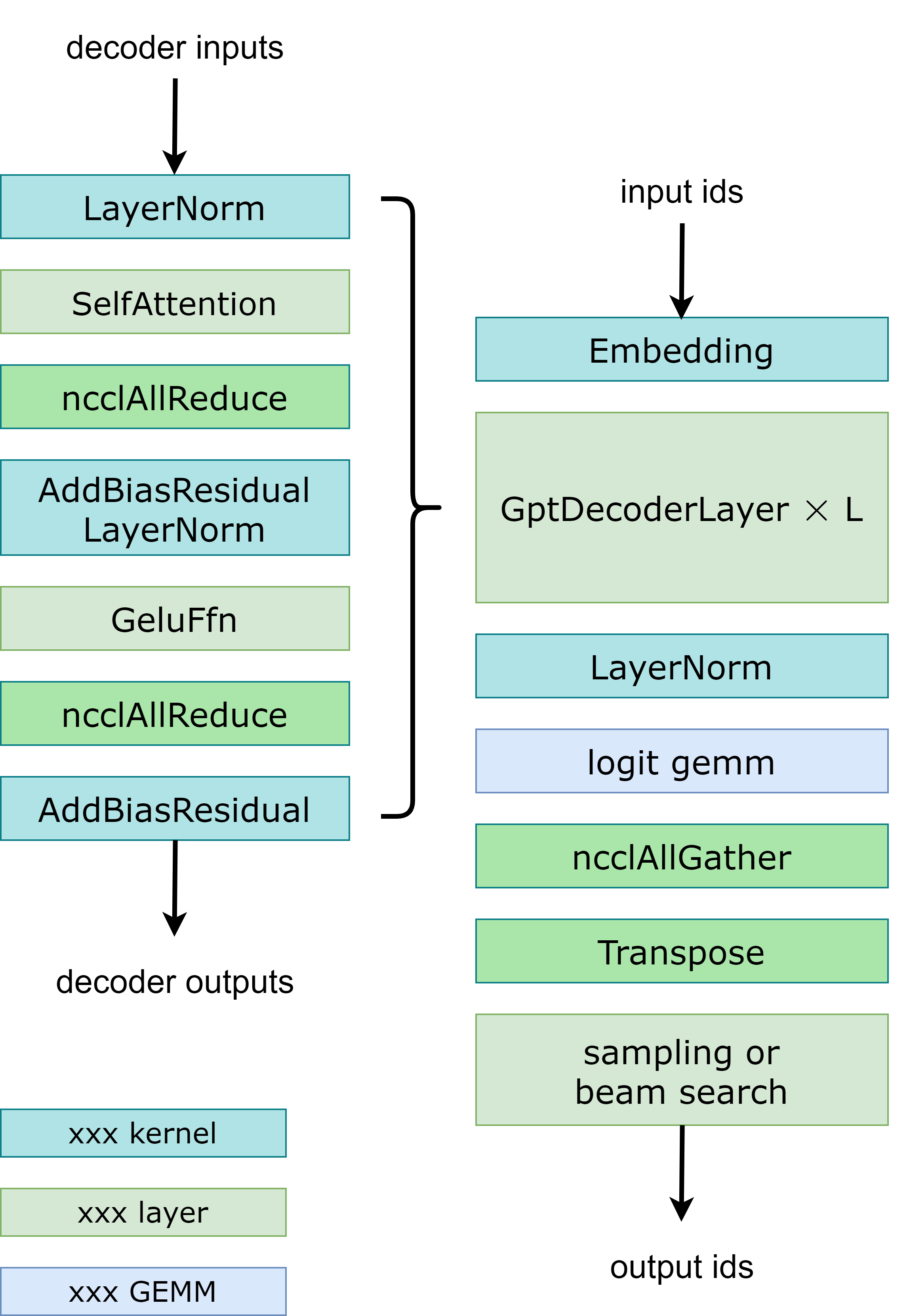
- 模型并行:在GPT模型中,FasterTransormer同时提供张量并行和流水线并行。 对于张量并行,FasterTransformer 遵循了 Megatron 的思想。 对于自注意力块和前馈网络块,我们按行拆分第一个矩阵乘法的权重,按列拆分第二个矩阵乘法的权重。 通过优化,我们可以将每个Transformer块的归约操作减少到 2 次。 工作流程如Fig 3 所示。对于流水并行,FasterTransformer 将整个Batch的请求拆分为多个Micro Batch并隐藏通信气泡。 FasterTransformer 会针对不同情况自动调整微批量大小。 用户可以通过修改 gpt_config.ini 文件来调整模型并行度。 我们建议在节点内使用张量并行,在节点间使用流水并行,因为张量并行需要更多的 NCCL 通信。
- 多框架:FasterTransformer除了C上的源代码,还提供了TensorFlow op、PyTorch op和Triton backend。 目前TensorFlow op只支持单GPU,而PyTorch op和Triton backend支持多GPU和多节点。 FasterTransformer 还提供了一个工具,可以将 Megatron 的模型拆分并转换为二进制文件,然后 FasterTransformer 可以直接加载二进制文件,从而避免为模型并行而进行额外的模型拆分工作。
笔记¶
is_context_qk_buf_float_(是否对 GPT context QK GEMM 使用浮点累加)默认设置为 false。 如果您遇到与 GPT Context注意力模块相关的准确性问题,请尝试在 ParallelGpt.h 中启用它。
CUDA相关优化点解读¶
- TensorRT fused multi-head attention kernel: 和 BERT 一样对于 GPT 的 ContextSelfAttention,FasterTransformer 使用 TensorRT 的 fused multi-head attention kernel 将 batch GEMM,softmax, GEMM,transpose 等操作都合并成一个 cuda kernel,不仅可以减少数据搬提升带宽利用率还可以减少 kernel launch 的开销。在 GPT 中对应了如下的实现:https://github.com/NVIDIA/FasterTransformer/blob/main/src/fastertransformer/layers/attention_layers/GptContextAttentionLayer.h 。然后在 GPT 的 DecoderLayer 实现中被调用:https://github.com/NVIDIA/FasterTransformer/blob/main/src/fastertransformer/models/multi_gpu_gpt/ParallelGptContextDecoder.cc#L547 。
- AddBiasResidualLayerNorm:在 Decoder 中将 Attention 的最后一个 Linear 的 bias_add,残差连接(elementwise_add)以及 LayerNorm 合并成一个 AddBiasResidualLayerNorm Kernel,降低 Kernel Launch 开销以及提升访问带宽。对应到 FasterTransformer中的代码实现在:https://github.com/NVIDIA/FasterTransformer/blob/main/src/fastertransformer/kernels/layernorm_kernels.cu#L24 。
- GeluFFN:从Fig1中的示意图可以看到 GeluFFN 包含两个 Linear 层,中间夹了一个 GeLU 的激活函数,这里做的优化是把第一个 Linear 层的 bias_add 和 GeLU 激活函数 fuse 到一起,也就是 AddBiasGeLU Kernel。对应到 FasterTransformer 的代码在:https://github.com/NVIDIA/FasterTransformer/blob/main/src/fastertransformer/kernels/activation_kernels.cu#L401 。
- AddBiasResidual:从Fig1的示意图可以看到,Decoder的最后一层就是 AddBiasResidual,这个Kernel就是把 bias_add 和 残差连接(element_wise add) 融合到一起。对应到 FasterTransformer 中的 https://github.com/NVIDIA/FasterTransformer/blob/main/src/fastertransformer/kernels/add_residual_kernels.cu#L22 。
- GEMM 试跑:和BERT一样仍然是在运行模型之前先试跑一下 GPT 网络中涉及到的GEMM的尺寸,并且保存 GEMM 性能最高的超参数配置,这个对于 cublas 和 cutlass 实现的卷积应该都是成立的。对应到 FasterTransformer中的:https://github.com/NVIDIA/FasterTransformer/blob/main/src/fastertransformer/models/multi_gpu_gpt/gpt_gemm.cc 。
- 高效的 LayerNorm:在 TensorFlow 里面 LayerNorm 是零碎的 Kernel 拼接的,在 FasterTransformer 中实现了一个 LayerNorm Kernel 来完成这个功能。实际上 PyTorch/OneFlow 等框架也有 LayerNorm Kernel,并且 OneFlow 的 LayerNorm 性能最强,可以看:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/443026261 。
- GEMM 的 FP16 累加:上面提到 is_context_qk_buf_float_ 参数,在 GPT 的 fp8 实现中,默认使用 GEMM 的 FP16 累加而非 FP32 累加,进一步提升性能,但是也可能带来精度问题。https://github.com/NVIDIA/FasterTransformer/blob/6ea1c77c7fabf1a046463eceddce1839efc63e60/src/fastertransformer/models/gpt_fp8/GptFP8.h#L47 ,最近我做一个大模型的推理工作时也发现如果基于 cutlass 的 gemm 使用 FP16 累加,最后生成的结果会部分乱码,所以这个优化必须用环境变量或者类似于这里用一个单独的参数来控制。
和通信相关的实现以及shared_context相关的优化这里就不提了,代码的可读性比较差,我个人建议有需要的读者学习下某些kernel的实现即可。
FasterTransformer 优点¶
从之前对 BERT 的优化点介绍以及这里对 GPT 的优化点介绍,我们可以发现 FasterTransformer集成了大量针对Transformer架构的优化,并且实现了各种Transformer架构中常见的各种fuse pattern对应的kernel。并且较为完整的支持了Transformer架构的int8推理,整体的性能始终保持在一个SOTA水平。对于我这种入门CUDA优化的学习者来说有一定的学习意义。此外,FasterTransformer也将实现的这些组件注册到TensorFlow,PyTorch等框架中使得读者可以对常见的Transformer架构进行推理。
FasterTransformer 缺点¶
CUDA Kernel之外的代码写得很抽象,特别对于多卡模式来说需要用户手动管理通信和模型切分,这个门槛是很高的。如果用户想基于FasterTreansformer这个框架实现新的Transformer架构的网络会非常困难,必须要非常了解FasterTransformer才可以。除了要手动管理通信以及模型切分之外,如果用户的新模型中出现了新的组件不仅要实现CUDA Kernel还需要手动管理内存的申请和释放,比如GPT的内存申请和释放:https://github.com/NVIDIA/FasterTransformer/blob/main/src/fastertransformer/models/multi_gpu_gpt/ParallelGpt.cc#L96-L270 稍微不注意就可能内存泄露。最近试跑了一个第三方模型的FasterTransformer实现,就出现了类似的问题。
个人认为 FasterTransformer 的整体架构实现的用户体验类似于 “九转大肠”,易用性方面我还是比较看好 PyTorch ,OneFlow 等将内存管理,通信集成到框架底层用户新增模型只需要关心自定义 CUDA Kernel 的传统深度学习框架。个人建议可以学习下 FasterTransformer 某些 CUDA Kernel 实现,但基于这个框架来搭建应用要慎重。如果基于 PyTorch,OneFlow 等框架能将大量的 Transformer 架构性能追平甚至超越 FasterTransformer 就完全没必要折磨自己。
总结¶
这里总结了一下 FasterTransformer 里面和 CUDA Kernel相关的优化技巧,并且给出了Kernel实现的位置,并从易用性,性能多方便对比了 FasterTransformer 和 PyTorch/OneFlow 等框架的优缺点,供大家参考学习。
本文总阅读量次