前言¶
最近在做低照度图像恢复时,发现了一个充满知识的github工程:点这里,里面有一篇论文,《Adaptive Local Tone Mapping Based on Retinex for High Dynamic Range Images》,它结合传统的Retinex技术提出了全局自适应和局部自适应的HDR实现过程,这里是参考了作者的matlab代码写出了暴力版本的代码实现,在720p的图像上处理速度为68ms/张。论文的讲解不是很好翻译,大家可以去查看原始论文,我也没怎么读啦。。。论文地址在这里:http://koasas.kaist.ac.kr/bitstream/10203/172985/1/73275.pdf ,我只是实现了论文中的一小部分,就是全局自适应,发现对于低照度的彩色图像恢复效果很好。
原理¶

首先引入了这个公式,这些符号代表些啥呢?L_g(x,y)是全自适应输出的结果,我们这里就是需要得到它,L_w(x,y)代表输入图像的luminance值(亮度值),L_{wmax}表示输入图像亮度值对的最大值,{L_w}横线 表示输入亮度对数的平均值。 然后:
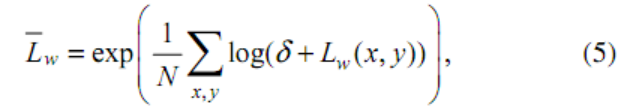
其中N表示像素的总数,而δ一般是个很小的值,其作用主要是为了避免对纯黑色像素进行log计算时数值溢出,这个问题在图像处理时非常常见。直接应用原文的话,(这段描述来自: https://www.cnblogs.com/Imageshop/p/9460334.html )上述算式的主要作用是:
The input world luminance values and the maximum luminance values are divided by the log-average luminance of he scene. This enables (4) to adapt to each scene. As the log-verage luminance converges to the high value, the function converges from the shape of the logarithm function to the near function. Thus, scenes of the low log-average luminance reboosted more than scenes with high values. As a result, the overall scene luminance values are adequately compressed in ccordance with the log-average luminance of the scene.
特别注意的是 scenes of the low log-average luminance reboosted more than scenes with high values. 这句话,他的意思是说低照度的亮度部分比高照度的部分要能得到更大程度的提升,所以对于低照度图,上述公式能起到很好的增强作用。而算式中使用了全局的对数平均值,这就有了一定的自适应性。
代码实现¶
我暂时只实现了c++暴力版本,代码如下:
#include "function.h"
void simple_color_balance(float ** input_img, float ** out_img, int rows, int cols) {
float max_value = 0;
float min_value = 256;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
max_value = max(max_value,input_img[i][j]);
min_value = min(min_value, input_img[i][j]);
}
}
if (max_value <= min_value) {
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
out_img[i][j] = max_value;
}
}
}
else {
float scale = 255.0 / (max_value - min_value);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (input_img[i][j] < min_value) {
out_img[i][j] = 0;
}
else if (input_img[i][j] > max_value) {
out_img[i][j] = 255;
}
else {
out_img[i][j] = scale * (input_img[i][j] - min_value);
}
}
}
}
}
int HDR(cv::Mat input_img, cv::Mat out_img) {
int rows = input_img.rows;
int cols = input_img.cols;
//DouImg
float ***DouImg;
DouImg = new float **[rows];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
DouImg[i] = new float *[cols];
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
DouImg[i][j] = new float[3];
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
DouImg[i][j][0] = (float)input_img.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[0];
DouImg[i][j][1] = (float)input_img.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[1];
DouImg[i][j][2] = (float)input_img.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[2];
}
}
//Lw
float **Lw;
Lw = new float *[rows];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
Lw[i] = new float [cols];
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
Lw[i][j] = 0;
}
}
//B
float **B;
B = new float *[rows];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
B[i] = new float[cols];
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
B[i][j] = (float)input_img.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[0];
}
}
//G
float **G;
G = new float *[rows];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
G[i] = new float[cols];
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
G[i][j] = (float)input_img.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[1];
}
}
//R
float **R;
R = new float *[rows];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
R[i] = new float[cols];
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
R[i][j] = (float)input_img.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[2];
}
}
//Lwmax
float Lwmax = 0.0;
//Lw
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
Lw[i][j] = 0.299 * R[i][j] + 0.587 * G[i][j] + 0.114 * B[i][j];
if (Lw[i][j] == 0) {
Lw[i][j] = 1;
}
Lwmax = max(Lw[i][j], Lwmax);
}
}
//Lw_sum
float Lw_sum = 0;
//log_Lw
float **log_Lw;
log_Lw = new float *[rows];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
log_Lw[i] = new float[cols];
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
log_Lw[i][j] = log(0.001 + Lw[i][j]);
Lw_sum += log_Lw[i][j];
}
}
//Lwaver
float Lwaver = exp(Lw_sum / (rows * cols));
//Lg
float **Lg;
Lg = new float *[rows];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
Lg[i] = new float[cols];
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
Lg[i][j] = log(Lw[i][j] / Lwaver + 1) / log(Lwmax / Lwaver + 1);
}
}
//gain
float **gain;
gain = new float *[rows];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
gain[i] = new float[cols];
}
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
gain[i][j] = Lg[i][j] / Lw[i][j];
}
}
//gain*B, gain*G, gain*R
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
B[i][j] *= gain[i][j];
G[i][j] *= gain[i][j];
R[i][j] *= gain[i][j];
}
}
simple_color_balance(B, B, rows, cols);
simple_color_balance(G, G, rows, cols);
simple_color_balance(R, R, rows, cols);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < cols; j++){
out_img.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[0] = uchar((int)B[i][j]);
out_img.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[1] = uchar((int)G[i][j]);
out_img.at<Vec3b>(i, j)[2] = uchar((int)R[i][j]);
}
}
//Free
//DouImg
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
delete DouImg[i][j];
}
delete DouImg[i];
}
delete DouImg;
//Lw
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
delete[] Lw[i];
}
delete Lw;
//log_Lw
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
delete[] log_Lw[i];
}
delete log_Lw;
//B
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
delete[] B[i];
}
delete B;
//G
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
delete[] G[i];
}
delete G;
//R
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
delete[] R[i];
}
delete R;
//Lg
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
delete[] Lg[i];
}
delete Lg;
//gain
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
delete[] gain[i];
}
delete gain;
return 0;
}
#pragma once
#include "opencv2\opencv.hpp"
#include "cv.h"
#include "iostream"
#include "algorithm"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
void simple_color_balance(float ** input_img, float ** out_img, int rows, int cols);
int HDR(cv::Mat input_img, cv::Mat out_img);
优化版本出来了,我会再放上来,欢迎大家多交流。我的github:点这里
本文总阅读量次