1. 前言¶
上一篇推文如何让你的YOLOV3模型更小更快? 给大家介绍了一下利用BN层的\gamma参数对YOLOV3检测模型进行剪枝,最终获得了2倍的速度增涨。但需要注意的是,这个剪枝有一些缺点,例如剪枝剪得不够极限,可能还有一些冗余通道存在,另外和shortcut层相邻的卷积层以及上采样层前的卷积层并没有剪枝。并且剪枝之后模型的通道数会变成一些奇怪的数字例如23,这在推理过程中会浪费一部分硬件的内存,并对模型的推理速度产生影响。最后,很多人在简单的检测场景中(例如一个类别的检测)倾向使用YOLOV3-Tiny这个小模型,我们可以通过剪枝使得这个模型更小,但上次的项目是不支持的。基于上面的需求,coldlarry开发了一个完整的YOLOV3剪枝库,可以满足刚刚提高的所有需求,代码地址如下:https://github.com/coldlarry/YOLOv3-complete-pruning。
2. 项目整体把握¶
这个项目仍然是基于U版的YOLOV3,并且可以加载DarkNet(无论是官方版本还是AlexeyAB版本)YOLOV3权重,所以使用起来非常方便,下面我们来看看这个项目里面的一些文件或者文件夹是在做什么吧。
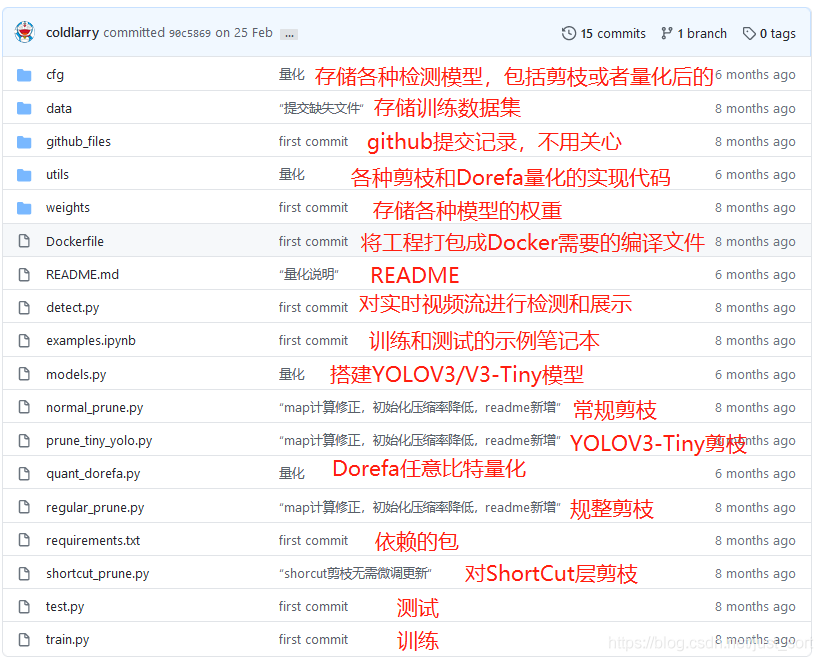
关于Dorefa量化以及低比特量化后面我会单独讲,这篇文章主要讲一下这个工程中的4种剪枝方法,这里先看一下这4种剪枝方法的特点:

3. 正常剪枝&规整剪枝¶
正常剪枝在昨天的推文中已经介绍过了,请移步如何让你的YOLOV3模型更小更快? ,代码实现在utils/prune_utils.py中,和昨天讲解的代码完全一样。我们重点看一下规整剪枝是什么意思?
在工程根目录下的regular_prune.py实现了规整剪枝,代码地址为:https://github.com/coldlarry/YOLOv3-complete-pruning/blob/master/regular_prune.py ,它的代码和上篇推文讲到的正常剪枝几乎完全一致,只是多了一个限制条件,代码解析如下:
# 记录了每个CBL层最少需要保留的通道数,都是2^n
filter_switch=[8,16,32,64,128,256,512,1024]
def prune_and_eval(model, sorted_bn, percent=.0):
model_copy = deepcopy(model)
thre_index = int(len(sorted_bn) * percent)
#获得α参数的阈值,小于该值的α参数对应的通道,全部裁剪掉
thre = sorted_bn[thre_index]
print(f'Channels with Gamma value less than {thre:.4f} are pruned!')
remain_num = 0
for idx in prune_idx:
bn_module = model_copy.module_list[idx][1]
mask = obtain_bn_mask(bn_module, thre)
mask_cnt=int(mask.sum())
# mask_cnt=0代表这一个CBL中所有的BN层权重都小于阈值,本来该全部剪掉,但因为是规整剪枝,所以保留权重最大的8个通道
if mask_cnt==0:
this_layer_sort_bn=bn_module.weight.data.abs().clone()
sort_bn_values= torch.sort(this_layer_sort_bn)[0]
bn_cnt=bn_module.weight.shape[0]
this_layer_thre=sort_bn_values[bn_cnt-8]
mask = obtain_bn_mask(bn_module, this_layer_thre)
else:
# 如果剪枝的通道数<这一层预设的规整通道数,就少剪枝一些通道,使得其通道恰好为预设的规整通道数
for i in range(len(filter_switch)):
if mask_cnt<=filter_switch[i]:
mask_cnt=filter_switch[i]
break
this_layer_sort_bn=bn_module.weight.data.abs().clone()
sort_bn_values= torch.sort(this_layer_sort_bn)[0]
bn_cnt=bn_module.weight.shape[0]
this_layer_thre=sort_bn_values[bn_cnt-mask_cnt]
mask = obtain_bn_mask(bn_module, this_layer_thre)
remain_num += int(mask.sum())
bn_module.weight.data.mul_(mask)
with torch.no_grad():
mAP = eval_model(model_copy)[1].mean()
print(f'Number of channels has been reduced from {len(sorted_bn)} to {remain_num}')
print(f'Prune ratio: {1-remain_num/len(sorted_bn):.3f}')
print(f'mAP of the pruned model is {mAP:.4f}')
return thre
因此,规整剪枝就是让网络层的通道数剪枝之后仍然是预先设定的2^n这种形式,有利于模型的推理速度提升以及内存占用降低。
4. 极限剪枝¶
我们知道在正常剪枝和规整剪枝时它们都没有对shortcut层前的卷积层以及上采样层前的卷积层进行剪枝,下面的代码展示了常规/规整剪枝忽略了哪些层如下:
def parse_module_defs(module_defs):
CBL_idx = []#Conv+BN+ReLU
Conv_idx = []#Conv
for i, module_def in enumerate(module_defs):
if module_def['type'] == 'convolutional':
if module_def['batch_normalize'] == '1':
CBL_idx.append(i)
else:
Conv_idx.append(i)
ignore_idx = set()#哪些层不需要剪枝
for i, module_def in enumerate(module_defs):
# 忽略shortcut层前面邻接的卷积层
if module_def['type'] == 'shortcut':
ignore_idx.add(i-1)
identity_idx = (i + int(module_def['from']))
if module_defs[identity_idx]['type'] == 'convolutional':
ignore_idx.add(identity_idx)
elif module_defs[identity_idx]['type'] == 'shortcut':
ignore_idx.add(identity_idx - 1)
# 忽略上采样层
ignore_idx.add(84)
ignore_idx.add(96)
prune_idx = [idx for idx in CBL_idx if idx not in ignore_idx]
# 返回CBL组件的id,单独的Conv层的id,以及需要被剪枝的层的id
return CBL_idx, Conv_idx, prune_idx
因此,常规剪枝是剪得是不够"极限"的,因此在极限剪枝这个方法里面仅仅忽略上采样层前面卷积层(一共2个),shortcut相邻的卷积层全部参与剪枝,即实现了极限的YOLOV3剪枝,代码如下:
#short-cut剪枝
class opt():
model_def = "cfg/yolov3-hand.cfg"
data_config = "data/oxfordhand.data"
model = 'weights/last.pt'
#指定GPU
#torch.cuda.set_device(2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
model = Darknet(opt.model_def).to(device)
if opt.model:
if opt.model.endswith(".pt"):
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(opt.model, map_location=device)['model'])
else:
_ = load_darknet_weights(model, opt.model)
data_config = parse_data_cfg(opt.data_config)
valid_path = data_config["valid"]
class_names = load_classes(data_config["names"])
eval_model = lambda model:test(model=model,cfg=opt.model_def, data=opt.data_config)
obtain_num_parameters = lambda model:sum([param.nelement() for param in model.parameters()])
#这个不应该注释掉,等会要恢复
with torch.no_grad():
origin_model_metric = eval_model(model)
origin_nparameters = obtain_num_parameters(model)
'''
module_defs是一个列表,列表的每一项都是一个字典.贮存的只是并不生效的网络结构信息
例如{'type': 'convolutional', 'batch_normalize': '1', 'filters': '32', 'size': '3', 'stride': '1', 'pad': '1', 'activation': 'leaky'}
module_list是一个列表,列表的每一项都是一个列表,例如:
Sequential(
(conv_0): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
(batch_norm_0): BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
(leaky_0): LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1, inplace)
)
此时对列表索引0,结果为:Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1), padding=(1, 1), bias=False)
索引1,结果为:BatchNorm2d(32, eps=1e-05, momentum=0.1, affine=True, track_running_stats=True)
需要注意的是,module_list的数据类型其实是nn.ModuleList(),是可以真正访问的网络结构,通过访问该list,可以获得权重偏置等数据
'''
#{3: 1, 7: 5, 10: 7, 14: 12, 17: 14, 20: 17, 23: 20, 26: 23, 29: 26, 32: 29, 35: 32, 39: 37, 42: 39, 45: 42, 48: 45, 51: 48, 54: 51, 57: 54, 60: 57, 64: 62, 67: 64, 70: 67, 73: 70}
CBL_idx, Conv_idx, prune_idx,shortcut_idx,shortcut_all= parse_module_defs2(model.module_defs)
sort_prune_idx=[idx for idx in prune_idx if idx not in shortcut_idx]
#将所有要剪枝的BN层的α参数,拷贝到bn_weights列表
bn_weights = gather_bn_weights(model.module_list, sort_prune_idx)
#torch.sort返回二维列表,第一维是排序后的值列表,第二维是排序后的值列表对应的索引
sorted_bn = torch.sort(bn_weights)[0]
#避免剪掉所有channel的最高阈值(每个BN层的gamma的最大值的最小值即为阈值上限)
highest_thre = []
for idx in sort_prune_idx:
#.item()可以得到张量里的元素值
highest_thre.append(model.module_list[idx][1].weight.data.abs().max().item())
highest_thre = min(highest_thre)
# 找到highest_thre对应的下标对应的百分比
percent_limit = (sorted_bn==highest_thre).nonzero().item()/len(bn_weights)
print(f'Threshold should be less than {highest_thre:.4f}.')
print(f'The corresponding prune ratio is {percent_limit:.3f}.')
# 该函数有很重要的意义:
# ①先用深拷贝将原始模型拷贝下来,得到model_copy
# ②将model_copy中,BN层中低于阈值的α参数赋值为0
# ③在BN层中,输出y=α*x+β,由于α参数的值被赋值为0,因此输入仅加了一个偏置β
# ④很神奇的是,network slimming中是将α参数和β参数都置0,该处只将α参数置0,但效果却很好:其实在另外一篇论文中,已经提到,可以先将β参数的效果移到
# 下一层卷积层,再去剪掉本层的α参数
# 该函数用最简单的方法,让我们看到了,如何快速看到剪枝后的效果
def prune_and_eval(model, sorted_bn, percent=.0):
model_copy = deepcopy(model)
thre_index = int(len(sorted_bn) * percent)
#获得α参数的阈值,小于该值的α参数对应的通道,全部裁剪掉
thre1 = sorted_bn[thre_index]
print(f'Channels with Gamma value less than {thre1:.6f} are pruned!')
remain_num = 0
idx_new=dict()
for idx in prune_idx:
if idx not in shortcut_idx:
bn_module = model_copy.module_list[idx][1]
mask = obtain_bn_mask(bn_module, thre1)
#记录剪枝后,每一层卷积层对应的mask
# idx_new[idx]=mask.cpu().numpy()
idx_new[idx]=mask
remain_num += int(mask.sum())
bn_module.weight.data.mul_(mask)
#bn_module.bias.data.mul_(mask*0.0001)
else:
bn_module = model_copy.module_list[idx][1]
mask=idx_new[shortcut_idx[idx]]
idx_new[idx]=mask
remain_num += int(mask.sum())
bn_module.weight.data.mul_(mask)
#print(int(mask.sum()))
with torch.no_grad():
mAP = eval_model(model_copy)[0][2]
print(f'Number of channels has been reduced from {len(sorted_bn)} to {remain_num}')
print(f'Prune ratio: {1-remain_num/len(sorted_bn):.3f}')
print(f'mAP of the pruned model is {mAP:.4f}')
return thre1
percent = 0.5
threshold = prune_and_eval(model, sorted_bn, percent)
#****************************************************************
#虽然上面已经能看到剪枝后的效果,但是没有生成剪枝后的模型结构,因此下面的代码是为了生成新的模型结构并拷贝旧模型参数到新模型
#%%
def obtain_filters_mask(model, thre, CBL_idx, prune_idx):
pruned = 0
total = 0
num_filters = []
filters_mask = []
idx_new=dict()
#CBL_idx存储的是所有带BN的卷积层(YOLO层的前一层卷积层是不带BN的)
for idx in CBL_idx:
bn_module = model.module_list[idx][1]
if idx in prune_idx:
if idx not in shortcut_idx:
mask = obtain_bn_mask(bn_module, thre).cpu().numpy()
idx_new[idx]=mask
remain = int(mask.sum())
pruned = pruned + mask.shape[0] - remain
# if remain == 0:
# print("Channels would be all pruned!")
# raise Exception
# print(f'layer index: {idx:>3d} \t total channel: {mask.shape[0]:>4d} \t '
# f'remaining channel: {remain:>4d}')
else:
mask=idx_new[shortcut_idx[idx]]
idx_new[idx]=mask
remain= int(mask.sum())
pruned = pruned + mask.shape[0] - remain
if remain == 0:
print("Channels would be all pruned!")
raise Exception
print(f'layer index: {idx:>3d} \t total channel: {mask.shape[0]:>4d} \t '
f'remaining channel: {remain:>4d}')
else:
mask = np.ones(bn_module.weight.data.shape)
remain = mask.shape[0]
total += mask.shape[0]
num_filters.append(remain)
filters_mask.append(mask.copy())
#因此,这里求出的prune_ratio,需要裁剪的α参数/cbl_idx中所有的α参数
prune_ratio = pruned / total
print(f'Prune channels: {pruned}\tPrune ratio: {prune_ratio:.3f}')
return num_filters, filters_mask
num_filters, filters_mask = obtain_filters_mask(model, threshold, CBL_idx, prune_idx)
#CBLidx2mask存储CBL_idx中,每一层BN层对应的mask
CBLidx2mask = {idx: mask for idx, mask in zip(CBL_idx, filters_mask)}
def update_activation(i, pruned_model, activation, CBL_idx):
next_idx = i + 1
if pruned_model.module_defs[next_idx]['type'] == 'convolutional':
next_conv = pruned_model.module_list[next_idx][0]
conv_sum = next_conv.weight.data.sum(dim=(2, 3))
offset = conv_sum.matmul(activation.reshape(-1, 1)).reshape(-1)
if next_idx in CBL_idx:
next_bn = pruned_model.module_list[next_idx][1]
next_bn.running_mean.data.sub_(offset)
else:
next_conv.bias.data.add_(offset)
def prune_model_keep_size2(model, prune_idx, CBL_idx, CBLidx2mask):
pruned_model = deepcopy(model)
activations = []
for i, model_def in enumerate(model.module_defs):
if model_def['type'] == 'convolutional':
activation = None
if i in prune_idx:
mask = torch.from_numpy(CBLidx2mask[i]).cuda()
bn_module = pruned_model.module_list[i][1]
bn_module.weight.data.mul_(mask)
activation = F.leaky_relu((1 - mask) * bn_module.bias.data, 0.1)
update_activation(i, pruned_model, activation, CBL_idx)
bn_module.bias.data.mul_(mask)
activations.append(activation)
if model_def['type'] == 'shortcut':
actv1 = activations[i - 1]
from_layer = int(model_def['from'])
actv2 = activations[i + from_layer]
activation = actv1 + actv2
update_activation(i, pruned_model, activation, CBL_idx)
activations.append(activation)
if model_def['type'] == 'route':
from_layers = [int(s) for s in model_def['layers'].split(',')]
if len(from_layers) == 1:
activation = activations[i + from_layers[0]]
update_activation(i, pruned_model, activation, CBL_idx)
else:
actv1 = activations[i + from_layers[0]]
actv2 = activations[from_layers[1]]
activation = torch.cat((actv1, actv2))
update_activation(i, pruned_model, activation, CBL_idx)
activations.append(activation)
if model_def['type'] == 'upsample':
activation = torch.zeros(int(model.module_defs[i - 1]['filters'])).cuda()
activations.append(activation)
if model_def['type'] == 'yolo':
activations.append(None)
return pruned_model
pruned_model = prune_model_keep_size2(model, prune_idx, CBL_idx, CBLidx2mask)
with torch.no_grad():
mAP = eval_model(pruned_model)[0][2]
print('after prune_model_keep_size map is {}'.format(mAP))
#获得原始模型的module_defs,并修改该defs中的卷积核数量
compact_module_defs = deepcopy(model.module_defs)
for idx, num in zip(CBL_idx, num_filters):
assert compact_module_defs[idx]['type'] == 'convolutional'
compact_module_defs[idx]['filters'] = str(num)
# for item_def in compact_module_defs:
# print(item_def)
compact_model = Darknet([model.hyperparams.copy()] + compact_module_defs).to(device)
compact_nparameters = obtain_num_parameters(compact_model)
init_weights_from_loose_model(compact_model, pruned_model, CBL_idx, Conv_idx, CBLidx2mask)
random_input = torch.rand((16, 3, 416, 416)).to(device)
def obtain_avg_forward_time(input, model, repeat=200):
model.eval()
start = time.time()
with torch.no_grad():
for i in range(repeat):
output = model(input)
avg_infer_time = (time.time() - start) / repeat
return avg_infer_time, output
pruned_forward_time, pruned_output = obtain_avg_forward_time(random_input, pruned_model)
compact_forward_time, compact_output = obtain_avg_forward_time(random_input, compact_model)
# 在测试集上测试剪枝后的模型, 并统计模型的参数数量
with torch.no_grad():
compact_model_metric = eval_model(compact_model)
# 比较剪枝前后参数数量的变化、指标性能的变化
metric_table = [
["Metric", "Before", "After"],
["mAP", f'{origin_model_metric[0][2]:.6f}', f'{compact_model_metric[0][2]:.6f}'],
["Parameters", f"{origin_nparameters}", f"{compact_nparameters}"],
["Inference", f'{pruned_forward_time:.4f}', f'{compact_forward_time:.4f}']
]
print(AsciiTable(metric_table).table)
# 生成剪枝后的cfg文件并保存模型
pruned_cfg_name = opt.model_def.replace('/', f'/prune_{percent}_')
#由于原始的compact_module_defs将anchor从字符串变为了数组,因此这里将anchors重新变为字符串
for item in compact_module_defs:
if item['type']=='yolo':
item['anchors']='10,13, 16,30, 33,23, 30,61, 62,45, 59,119, 116,90, 156,198, 373,326'
pruned_cfg_file = write_cfg(pruned_cfg_name, [model.hyperparams.copy()] + compact_module_defs)
print(f'Config file has been saved: {pruned_cfg_file}')
compact_model_name = 'weights/yolov3_hand_shortcut_pruning_'+str(percent)+'percent.weights'
save_weights(compact_model, path=compact_model_name)
print(f'Compact model has been saved: {compact_model_name}')
对上面的代码还有疑问的请移步前一个推文,有逐行的代码详解,通过极限剪枝,理论上可以剪枝掉YOLOV3更多的参数获得进一步加速。
5. Tiny剪枝¶
这就没什么好说的了,和YOLOV3剪枝只有解析模型的时候有一点差别,即生成CBL_idx,Conv_idx,prune_idx的函数针对YOLOV3-Tiny的模型结构做了一个小变化,代码如下:
def parse_module_defs(module_defs):
CBL_idx = []
Conv_idx = []
for i, module_def in enumerate(module_defs):
if module_def['type'] == 'convolutional':
if module_def['batch_normalize'] == '1':
CBL_idx.append(i)
else:
Conv_idx.append(i)
ignore_idx = set()
# 只用忽略唯一一个上采样层前面的卷积层即可
ignore_idx.add(18)
prune_idx = [idx for idx in CBL_idx if idx not in ignore_idx]
return CBL_idx, Conv_idx, prune_idx
YOLOV3-Tiny的模型结构如下所示,可以帮助理解:
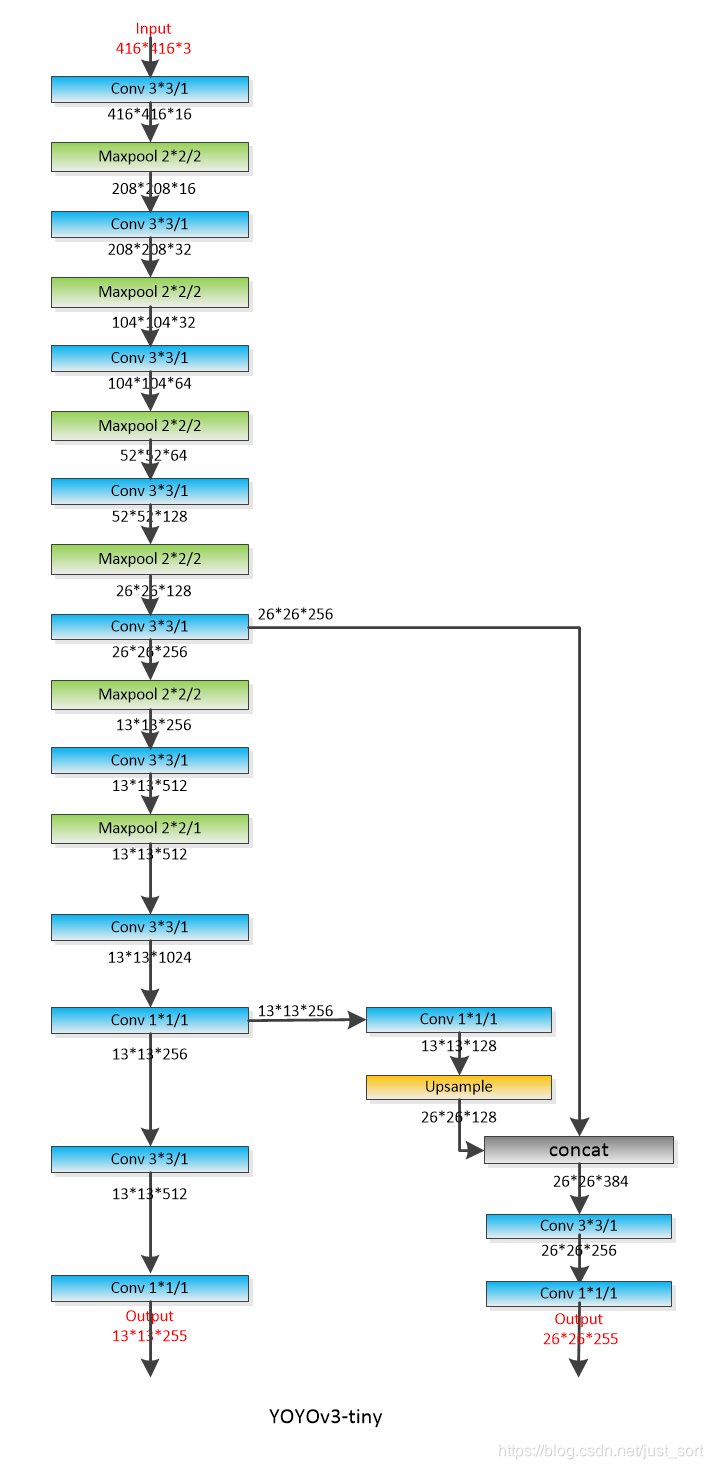
但建议慎重对YOLOV3-Tiny进行剪枝,笔者在手上的数据集实测过,对于一个类别训练出的YOLOV3模型不影响准确率的情况下基本不能剪掉任何参数,所以需要自己实测来判断自己的数据集是否剪枝后会对模型的准确率造成较大损害。
6. 结果¶
这些剪枝方法,获得的评价指标以及耗时情况如下图所示,仍然是基于Oxfard人手数据集:
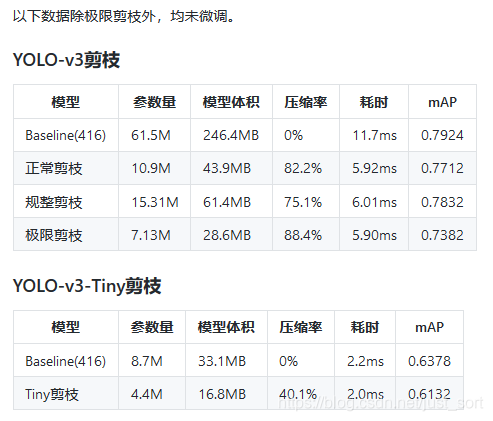
可以看到对YOLOV3-Tiny的剪枝意义不大,耗时虽然少了一点,但map降得比较多,猜测是因为YOLOV3-Tiny模型容量较小,BN的权重都偏大导致的。
7. 总结¶
这篇文章汇总了针对YOLOV3/YOLOV3-Tiny的几种典型剪枝算法,合理选用可以基本无痛的加速我们的网络,希望对大家有帮助。
欢迎关注GiantPandaCV, 在这里你将看到独家的深度学习分享,坚持原创,每天分享我们学习到的新鲜知识。( • ̀ω•́ )✧
有对文章相关的问题,或者想要加入交流群,欢迎添加BBuf微信:

为了方便读者获取资料以及我们公众号的作者发布一些Github工程的更新,我们成立了一个QQ群,二维码如下,感兴趣可以加入。

本文总阅读量次