【GiantPandaCV导语】本文是ONNX2Pytorch思路分享以及onnx-simplifier新版简要介绍。ONNX2Pytorch工具已经测试了onnx model zoo中的大量分类模型并转换正确,欢迎使用,github地址:https://github.com/BBuf/onnx2nn。GiantPandaCV几个月前遭受恶意举报,今天终于解除封印了。感谢众多粉丝们的长期等待和支持,我们会在此继续分享学习经验。
0x0. 背景¶
ONNX作为微软的神经网络模型的开放格式被各个框架广泛应用,包括Pytroch,TensorFlow,OneFlow,Keras,Paddle等多种深度学习训练框架。因此,之前一直在思考一个问题,一个TensorFlow/MxNet/Keras导出来的ONNX模型是否可以借助ONNX被Pytorch框架使用呢?ONNX的理想是作为所有训练框架模型的中间表示,那么我们只需要再实现ONNX到各个框架的逆转就可以完成这件事情了。本工程的目的即是尝试支持ONNX转换到Pytorch,主要为了锻炼算子对齐和更深入的了解ONNX。先放一下github地址:https://github.com/BBuf/onnx2nn,欢迎关注。这个工程复用了https://github.com/ToriML/onnx2pytorch的整体逻辑,解决了原始工程中遗留的大量BUG,支持了更多OP,实现了输入一个ONNX模型,返回一个torch.nn.Module对象,并将这个torch.nn.Module对应的Pytorch模型保存下来。
0x1. 思路¶
首先需要说明的是,在执行转换之前需要先过一遍onnx-simplifer对原始的ONNX模型进行简化,工程地址为:https://github.com/daquexian/onnx-simplifier 。为了使用方便,我将这个工具直接接入到了本工程,在后面的使用方法中可以看到。
然后这和项目的思路是非常简单的,直接遍历ONNX模型的计算节点(也即OP),把每个OP一对一的转换到Pytorch就可以了。核心代码地址为:https://github.com/BBuf/onnx2nn/blob/master/onnx2pytorch/convert/operations.py#L20-L181。简单截图说明一下:
def convert_operations(onnx_model, batch_dim=0):
"""
Convert onnx model operations. Yields onnx's operator_id, opeartor_name and
converted pytorch operator.
Parameters
----------
onnx_model: onnx.ModelProto
Loaded onnx model.
batch_dim: int
Usually 0 for computer vision models and 1 for NLP models.
Returns
-------
iterator: (op_id, op_name, op)
"""
weights = {tensor.name: tensor for tensor in onnx_model.graph.initializer}
for i, node in enumerate(onnx_model.graph.node):
# extract only useful inputs
params = [weights[par_name] for par_name in node.input if par_name in weights]
if node.op_type == "Conv":
op = convert_layer(node, "Conv", params)
elif node.op_type == "Relu":
op = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
elif node.op_type == "LeakyRelu":
op = nn.LeakyReLU(**extract_attributes(node), inplace=True)
elif node.op_type == "Sigmoid":
op = nn.Sigmoid()
elif node.op_type == "MaxPool":
op = convert_layer(node, "MaxPool")
elif node.op_type == "AveragePool":
op = convert_layer(node, "AvgPool")
elif node.op_type == "Flatten":
op = Flatten(**extract_attributes(node))
elif node.op_type == "Gemm":
op = convert_linear_layer(node, params)
op.feature_dim = batch_dim + 1 # Necessary for transformers
elif node.op_type == "BatchNormalization":
op = convert_batch_norm_layer(node, params=params)
elif node.op_type == "InstanceNormalization":
op = convert_instance_norm_layer(node, params=params)
elif node.op_type == "Concat":
op = Concat(**extract_attributes(node))
else
pass
op_name = "{}_{}".format(node.op_type, node.output[0])
op_id = node.output[0]
yield op_id, op_name, op
可以看到通过遍历ONNX模型的所有计算节点并获取每个节点的信息(输入参数以及各种attribute)之后将其用Pytorch的对应OP写出来就完成了转换过程。里面涉及到的每个OP的具体转换过程比如权重,attribute参数的提取以及对应Pytorch的实现等可以直接查看源码,这里不详细展开。
在获得每个ONNX计算节点对应的Pytorch OP之后,我们需要根据ONNX的计算节点反应的拓扑关系把所有的Pytorch OP组合成一个完整的Pytorch的模型,这部分的代码实现在:https://github.com/BBuf/onnx2nn/blob/master/onnx2pytorch/convert/model.py#L36-L131。
0x2. 一些需要注意的点¶
在执行ONNX2Pytorch的过程中需要注意一些由于Pytorch和ONNX OP实现不一致而导致模型转换失败的情况,下面列举一下:
-
非对称Padding问题。在对alexnet和google-net进行转换时发现它们的卷积或者Max Pooling层经常会出现非对称Padding的情况,由于Pytorch的卷积和最大池化操作不支持不对称Padding操作,所以这个时候为了保证转换的等价,需要将这个非对称Padding的OP拆成
nn.ConstantPad2d+无Padding的原始OP。 -
count_include_pad问题。在对inception-net进行转换时发现到了最后一个Avg Pooling层时出现了精度严重下降,经过Debug发现,Pytorch的Avg Pooling层的count_include_pad默认为True。如果这个时候也是非对称的Padding,那么按照上面的处理方法拆分成
ConstantPad2d+Avg Pooling之后会丢失精度,因为这种情况下Avg Pooling无法知晓自己Padding了多少元素。如下图所示:
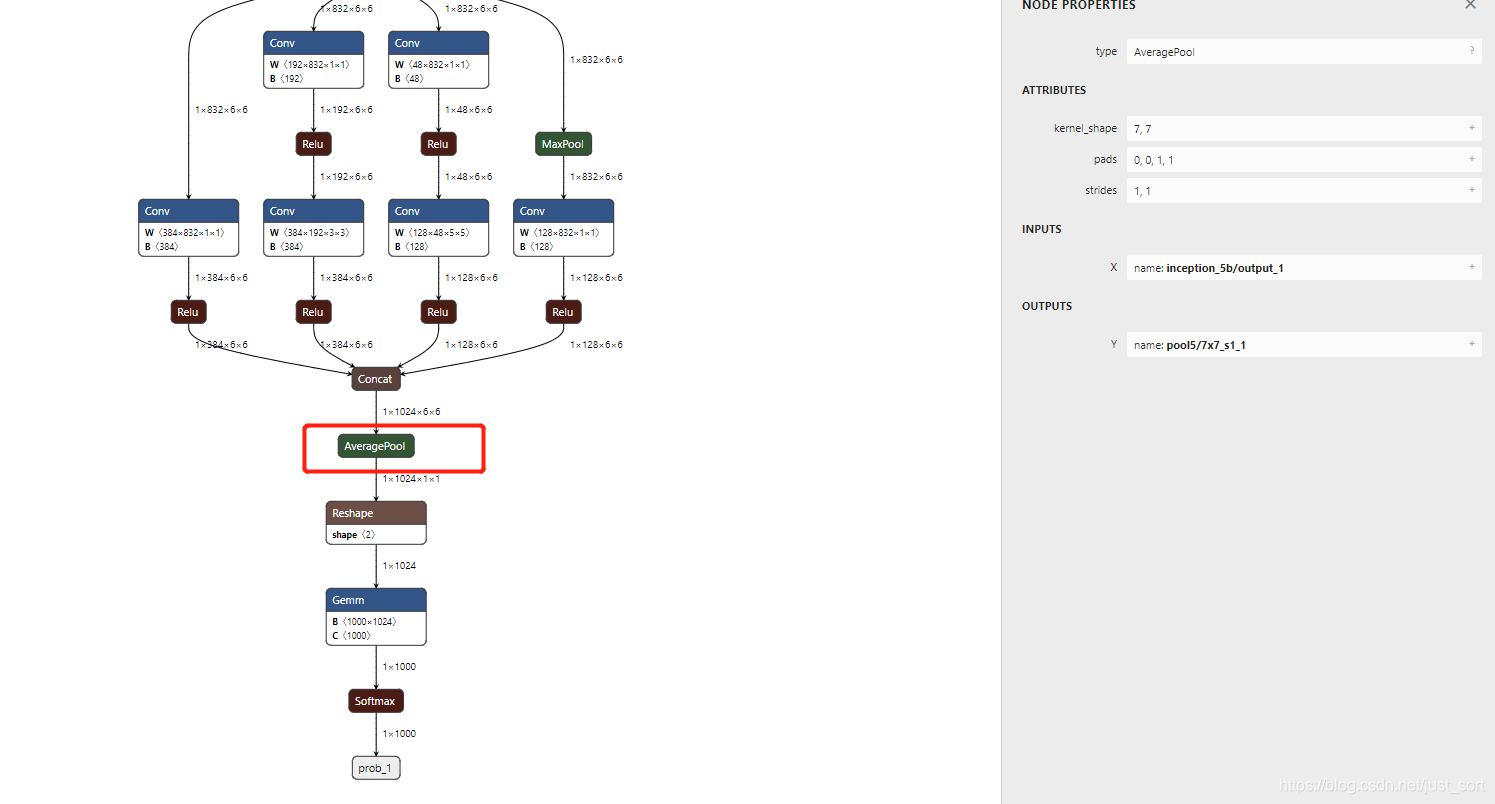
这个时候可以通过修改Kernel尺寸的方法来规避这个问题,在上面的例子中我们可以直接让kernel_shape等于(7-1=6,7-1=6)并且省掉新增常量Pad的操作。
这两点的代码实现在:https://github.com/BBuf/onnx2nn/blob/master/onnx2pytorch/convert/layer.py#L30-L91
- LRN层。在alexnet模型中有一个LRN层,这个层的参数长这样:
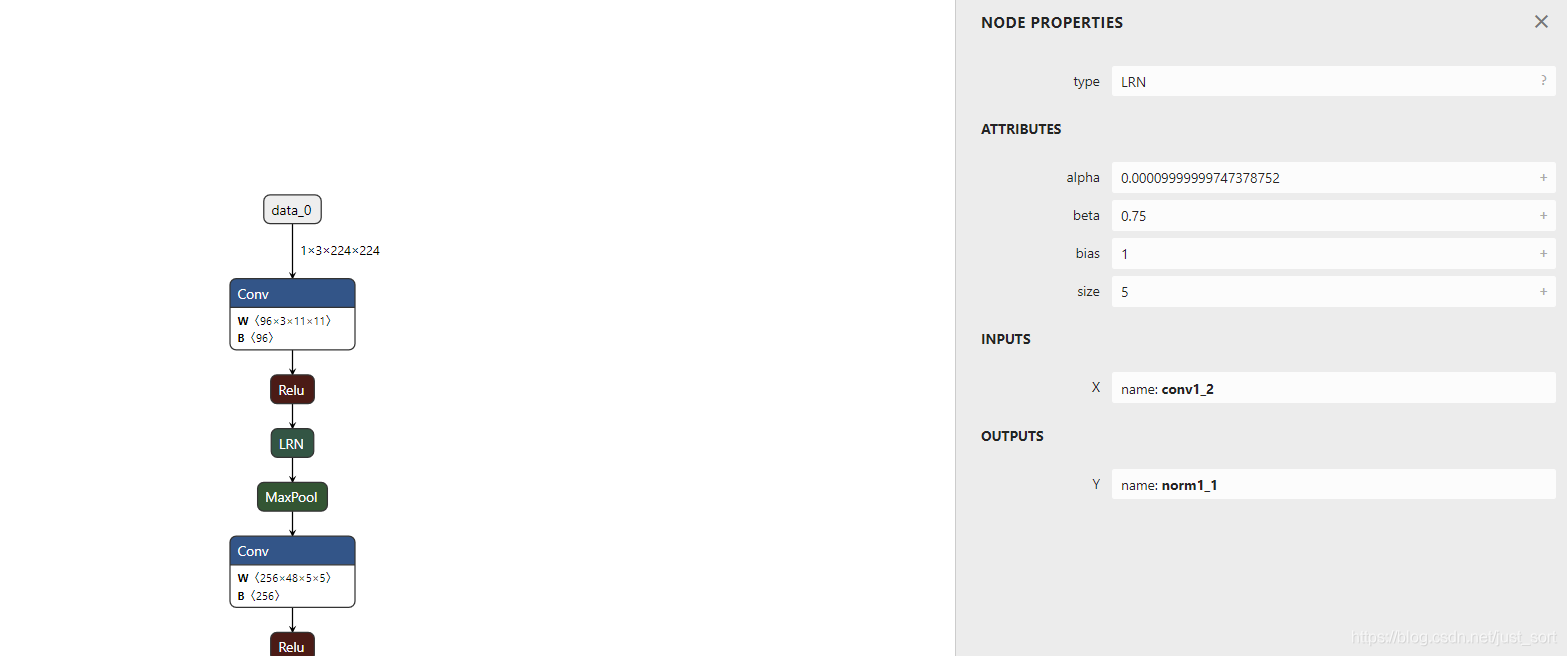
然后我们看一下Pytorch的LRN层的API:
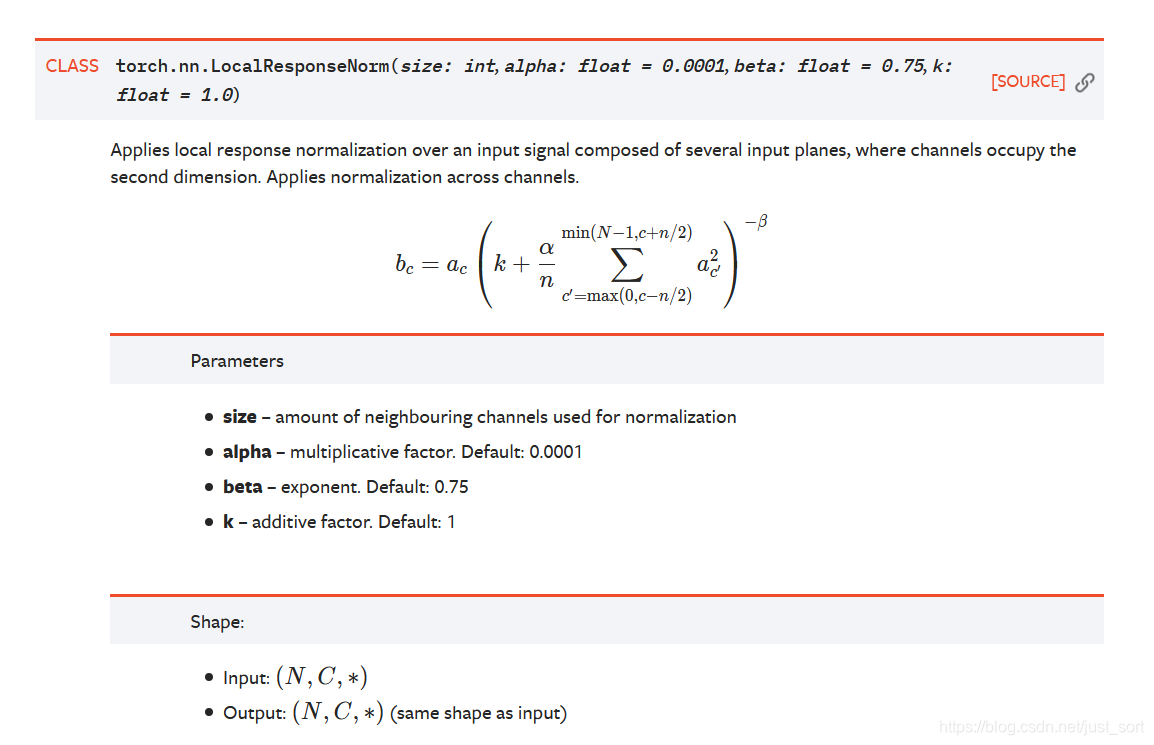
对比一下API的参数可以发现ONNX里面的bias对应的是Pytorch LRN里面的参数k,所以这里需要特殊处理一下,获取这个attribute的bias参数的值之后将其设为Pytorch LRN层里面的k参数的值。具体实现在:https://github.com/BBuf/onnx2nn/blob/master/onnx2pytorch/convert/attribute.py#L132-L139
0x3. onnx2nn工程介绍¶
0x3.1 代码结构¶
- onnx2pytorch onnx转pytorch代码实现
- onnx2pytorch.py onnx转pytorch测试代码
- convert_models.md 转换ONNX Model Zoo里面的模型对应的命令和结果记录
- README.md
0x3.2 运行环境¶
- pytorch >= 1.1.0
- onnx>=1.8.1
- onnxruntime>=1.6.0
- onnxoptimizer>=0.2.3
0x3.3 使用方法¶
使用下面的命令将各个训练框架导出的ONNX模型转换成Pytorch模型
python .\onnx2pytorch.py ...
参数列表如下:
--onnx_path字符串,必选参数,代表onnx模型的路径--pytorch_path字符串,必选参数,代表转换出的Pytorch模型保存路径--simplify_path字符串,可选参数,代表ONNX模型简化(例如删除Dropout和常量OP)后保存的ONNX模型路径--input_shape字符串,必选参数,代表ONNX模型的输入数据层的名字和维度信息
0x3.4使用示例¶
python .\onnx2pytorch.py --onnx_path .\models\mobilenetv2-7.onnx --simplify_path .\models\mobilenetv2-7-simplify.onnx --pytorch_path .\models\mobilenetv2-7.pth --input_shape input:1,3,224,224
0x3.5 模型转换失败处理方法¶
- 将
onnx2pytorch.py里面的model = convert.ConvertModel(onnx_model, debug=False)这行代码里面的debug设置False重新运行模型即可定位到转换失败的OP,然后你可以在工程提出issue或者自己解决然后给本工程PR。
0x3.6 已支持的ONNX OP¶
- Conv
- BatchNormalization
- GlobalAvgragePool
- AvgPool
- MaxPool
- BatchNorm
- Flatten
- Reshape
- Relu
- Add
- Gemm
- Sigmoid
- Mul
- Concat
- Resize (还有一些问题需要解决,当前版本支持固定倍数方法)
- Transpose
- LRN
- Clip
- Pad2d
- Split
- ReduceMean
0x3.7 已验证支持的模型¶
基于ONNXRuntime和Pytorch推理之后特征值mse小于1e-7,视为转换成功
分类模型¶
- zfnet512-9.onnx
- resnet50-v2-7.onnx
- mobilenetv2-7.onnx
- mobilenetv2-1.0.onnx
- bvlcalexnet-9.onnx
- googlenet-9.onnx
- squeezenet1.1-7.onnx
- shufflenet-v2-10.onnx
- inception-v1-9.onnx
- inception-v2-9.onnx
- vgg19-caffe2-9.onnx
- rcnn-ilsvrc13-9.onnx
检测模型¶
- yolov5s-simple.onnx
0x3.7 TODO¶
- 支持更多模型
- 重构工程,并解决某些模型转为Pytorch模型之后Netron可视化看不到某些OP的问题
- 一些部署工作,比如Keras导出的ONNX转为Pytorch模型后,二次导出ONNX递交给NCNN推理
0x4. onnx-simplifer最近更新¶
onnx-simplifer最近迎来了一次更新,这次更新是和onnxruntime一起更新的,小伙伴们要使用最新版本记得把onnxruntime更新到1.6.0哦。然后我去阅读了一下最新的onnx-simplifer,在上次的ONNX初探基础上,增加了一个递归函数fixed_point,功能就是递归执行func_a和fun_b直到模型稳定,代码如下:
# 递归执行func_a和func_b直到模型稳定
def fixed_point(x: T, func_a: Callable[[T], T], func_b: Callable[[T], T]) -> T:
"""
Run `func_a` and `func_b` on `x` until func_b(func_a(x)) == x
:param x:
:param func_a: A function satisfying func_a(func_a(x)) == func_a(x)
:param func_b: A function satisfying func_b(func_b(x)) == func_b(x)
:return: the x that satisfies func_b(func_a(x)) == x
"""
x = func_a(x)
x = func_b(x)
while True:
y = func_a(x)
if y == x:
# Since func_b(func_b(x)) == func_b(x),
# we are already at the fixed point if
# `y == x`
return x
x = y
y = func_b(x)
if y == x:
return x
x = y
我们看一下它是怎么应用的就可以了,注释如下:
def simplify(model: Union[str, onnx.ModelProto],
check_n: int = 0,
perform_optimization: bool = True,
skip_fuse_bn: bool = False,
input_shapes: Optional[TensorShapesWithOptionalKey] = None,
skipped_optimizers: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None,
skip_shape_inference=False,
input_data: Optional[Tensors] = None,
dynamic_input_shape: bool = False,
custom_lib: Optional[str] = None) -> Tuple[onnx.ModelProto, bool]:
"""
:param model: onnx ModelProto object or file path
:param check_n: The simplified model will be checked for `check_n` times by random inputs
:param perform_optimization: Whether to run onnx optimizer on the model
:param skip_fuse_bn: Skip fuse_bn_into_conv onnx optimizer
:param input_shapes: If the model has dynamic input shape, user must pass a fixed input shape
for generating random inputs and checking equality. (Also see "dynamic_input_shape" param)
:param skipped_optimizers: Skip some specific onnx optimizers
:param skip_shape_inference: Skip shape inference (sometimes shape inference will crash)
:param input_data: Feed custom input data for checking if needed
:param dynamic_input_shape: Indicates whether the input shape should be dynamic. Note that
input_shapes is also needed even if dynamic_input_shape is True,
the value of input_shapes will be used when generating random inputs for checking equality.
If 'dynamic_input_shape' is False, the input shape in simplified model will be overwritten
by the value of 'input_shapes' param.
:param custom_lib: onnxruntime custom ops's shared library
:return: A tuple (simplified model, success(True) or failed(False))
"""
if input_shapes is None:
input_shapes = {}
if input_data is None:
input_data = {}
if type(model) == str:
# 加载ONNX模型
model = onnx.load(model)
assert(isinstance(model, onnx.ModelProto))
# 检查ONNX模型格式是否正确,图结构是否完整,节点是否正确等
onnx.checker.check_model(model)
# 深拷贝一份原始ONNX模型
model_ori = copy.deepcopy(model)
input_names = get_input_names(model)
for input_name, data in input_data.items():
if input_name not in input_names:
raise RuntimeError(
'The model doesn\'t have input named "{}"'.format(input_name))
shape = list(input_data[input_name].shape)
# special case for single constant variables (with shape [])
if len(shape) == 0:
shape = [input_data[input_name].size]
if input_name in input_shapes and shape != input_shapes[input_name]:
raise RuntimeError('The shape of input_data[{}] is not the same with input_shape[{}]'.format(
input_name, input_name))
elif input_name not in input_shapes:
input_shapes[input_name] = shape
# 检查核对输入节点
updated_input_shapes = check_and_update_input_shapes(model, input_shapes)
def infer_shapes_and_optimize(model: onnx.ModelProto) -> onnx.ModelProto:
# 做ONNX模型节点形状推断
def infer_shapes_if_applicable(model: onnx.ModelProto) -> onnx.ModelProto:
if not skip_shape_inference:
model = infer_shapes(model)
return model
# 对ONNX模型进行optimizer
def optimize_if_applicable(model: onnx.ModelProto) -> onnx.ModelProto:
if perform_optimization:
model = optimize(model, skip_fuse_bn, skipped_optimizers)
return model
# 递归执行infer_shapes_if_applicable和optimize_if_applicable直到模型稳定
return fixed_point(model, infer_shapes_if_applicable, optimize_if_applicable)
def constant_folding(model: onnx.ModelProto) -> onnx.ModelProto:
# 获取模型的常量OP
const_nodes = get_constant_nodes(
model, dynamic_input_shape=dynamic_input_shape)
# 获取所有的常量OP以及原始输出OP的特征值
res = forward_for_node_outputs(model,
const_nodes,
input_shapes=updated_input_shapes,
input_data=input_data,
custom_lib=custom_lib)
# 清洗那些没有被onnxruntime推理的静态节点
const_nodes = clean_constant_nodes(const_nodes, res)
# 移除常量OP,获得简化后的ONNX模型
model = eliminate_const_nodes(model, const_nodes, res)
# 检查ONNX模型格式是否正确,图结构是否完整,节点是否正确等
onnx.checker.check_model(model)
return model
# 递归执行infer_shapes_and_optimize和constant_folding直到模型稳定
model = fixed_point(model, infer_shapes_and_optimize, constant_folding)
# 重写模型的输入shape
if not dynamic_input_shape:
for name, input_shape in updated_input_shapes.items():
for ipt in model.graph.input:
if ipt.name == name:
for i, dim in enumerate(ipt.type.tensor_type.shape.dim):
dim.dim_value = input_shape[i]
# 检查核对输入节点
check_ok = check(model_ori, model, check_n,
input_shapes=updated_input_shapes)
return model, check_ok
现在onnx-simplifer在简化过程中会递归的去推断shape,折叠常量,以及optimizer。所以这个程序比较依赖各个操作都不出错,如果某一步发生错误,可能有qia住的风险哦。使用最新版onnx-simplifer前切记更新onnxruntime到最新版本,否则使用model zoo里面的mobilenet模型就会引发qia住这一现象。
了解更多onnx-simplifer,比如执行流程,每一步再干什么请看ONNX初探的文章以及大老师发布的onnx simplifier 和 optimizer。
BBuf只是API搬运工,onnxoptimizer和onnx-simplifer的作者大老师才是yyds。
0x5. 推荐学习¶
之前写过和整理一些ONNX学习笔记,现在汇总如下,如果你是从模型部署来看ONNX,其实我个人认为看这些了解就差不多了,当然有新的想法我也会继续更新的(鸽。
0x6. 相关链接¶
- https://github.com/ToriML/onnx2pytorch
- https://github.com/daquexian/onnx-simplifier
- https://github.com/BBuf/onnx2nn
欢迎关注GiantPandaCV, 在这里你将看到独家的深度学习分享,坚持原创,每天分享我们学习到的新鲜知识。( • ̀ω•́ )✧
有对文章相关的问题,或者想要加入交流群,欢迎添加BBuf微信:

为了方便读者获取资料以及我们公众号的作者发布一些Github工程的更新,我们成立了一个QQ群,二维码如下,感兴趣可以加入。

本文总阅读量次